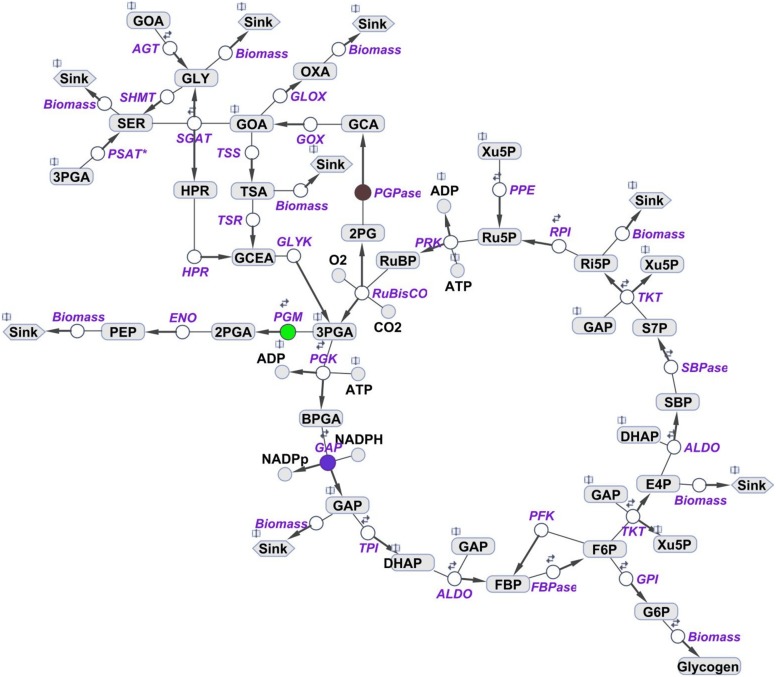
Figure 1. Scheme of primary carbon metabolism encoded as a kinetic model of Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942.
The model includes the Calvin-Benson cycle, glycogen synthesis, photorespiratory pathways, glycolysis, and sink reactions (representing the adjacent pathway and calculation of biomass production). Three reactions catalyzed by isozymes include phosphoglycerate mutases (green), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (blue), and phosphoglycolate phosphatase (red). Reversibility of a particular reaction is indicated by two small arrows. For further details, see File S1. Purple color shows involved enzymes: RuBisCO-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, PGK-phosphoglycerate kinase, GAP-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, TPI-triose phosphate isomerase, ALDO-aldolase, FBPase-fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase, PFK-phosphofructokinase, TKT-transketolase, SBPase-sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase, RPI-phosphopentose isomerase, PPE-phosphopentose epimerase, PRK-phosphoribulokinase, GPI-glucose-6-phosphat isomerase, PGPase-phosphoglycolate phosphatase, GOX-glycolate oxidase, SGAT-serine-glyoxylate transaminase, HPR-hydroxypyruvate reductase, GLYK-glycerate kinase, AGT-alanine-glyoxylate transaminase, TSS-tartronate semialdehyde synthase, TSA-tartronate semialdehyde reductase, SHMT-serine hydroxymethyltransferase, GLOX-glyoxylate oxidase, PSAT*-phosphoserine transaminase (3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase is, for simplicity, not implemented).