Figure 2.
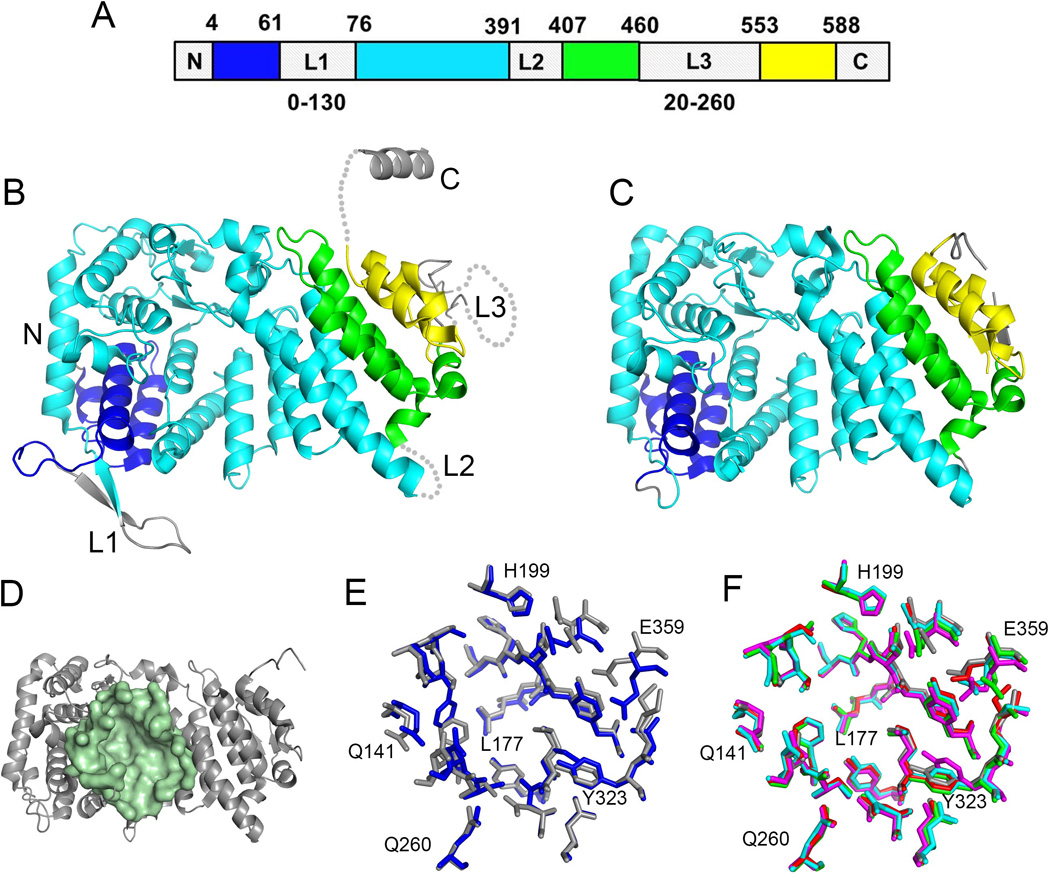
Structure of menin and the central cavity. A. Schematics of a sequence of human menin showing the location of elements of the folded core (structured segments are shown in blue, cyan, green and yellow) and location of three loops L1 to L3. The sequences and lengths of these loops vary significantly among menin homologs and the length for the most variable loops L1 and L3 is shown at the bottom. B. Crystal structure of human menin (PDB code 3U84) with color coding the same as in A. C. High resolution crystal structure of human menin obtained upon deletion or truncation of loops L1 – L3 and the C-terminus (4GPQ). D. Structure of human menin showing a central cavity; residues lining the cavity are shown in pale green. E. Superposition of residues in the central cavity of human menin (4GPQ, gray) and Nematostella menin (3RE2, blue). F. Comparison of conformations of residues lining the central cavity in apo menin (4GPQ, gray; 3U84, magenta) and menin fromthe complexes with bound protein ligands (4GQ6, red; 3U86, green; 3U85, cyan); selected residues are labeled.
