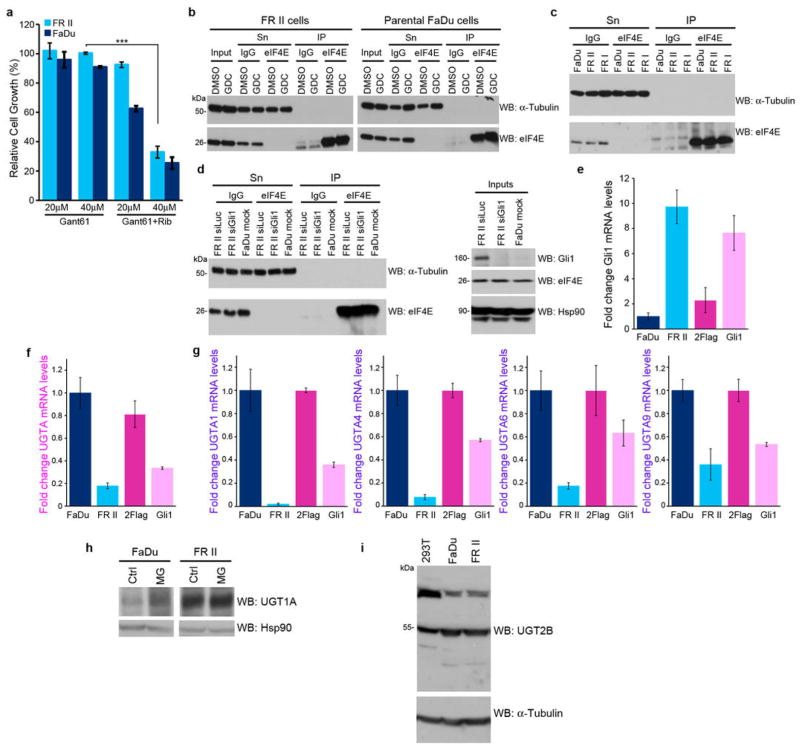
Figure 6.
Effects of modulation of Gli1 levels on UGT1A A. Effects of the direct Gli1 inhibitor GANT-61 on restoring ribavirin sensitivity (20 uM) in FRII cells. Effects are dependent on GANT-61 dose. B–D. Controls for eIF4E-ribavirin immunoprecipitations (IP) shown in Figures 1E and 3B. Inputs, supernatants (Sn) and IP controls for 3H ribavirin anti-eIF4E IPs are shown for GDC-0449 treated cells (B), FRII and FRI cells (C), and RNAi mediated knockdown of Gli1 (D). E–G. qPCR analysis of Gli1 (E) and UGT1A (F) using a pan-UGT1A primer or primers for specific UGT1As (G). mRNA levels were normalized to RNA Polymerase IIa. These findings are consistent with Extended Data Table 1 which indicates lower levels of UGT1A mRNA levels. Further, UGT1A3 and UGT1A8 decreased similarly (data not shown). Experiments were carried out in triplicate, at least three independent times. Average values are reported and error bars indicate standard deviations. These findings, that Gli1 elevation leads to reduce mRNA levels but increased protein levels are counter-intuitive. We hypothesize that Gli1 elevation increases protein stability of UGT1As (see below) and this leads to some sort of feedback mechanism leading to reduced UGT1As. Other scenarios are possible but the main point that Gli1 elevation leads to increased UGT1A protein production is clear. G. Gli1 increases UGT1A protein stability as shown by studies with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 and a pan-UGT1A antibody. Here, MG132 addition stabilizes levels of UGT1A in parental cells, but in FRII cells where levels are already increased, there is no further increase with MG132. This indicates that UGT1A proteins are already stabilized in the FRII cells. All results are representative of three independent experiments. H. Western blot analysis with a pan-UGT2B antibody indicates that UGT2B levels are unchanged in FRII relative to FaDu cells suggesting the glucuronidation effects are mediated mostly through the UGT1A family. Tubulin provides a loading control.