Fig. 6.
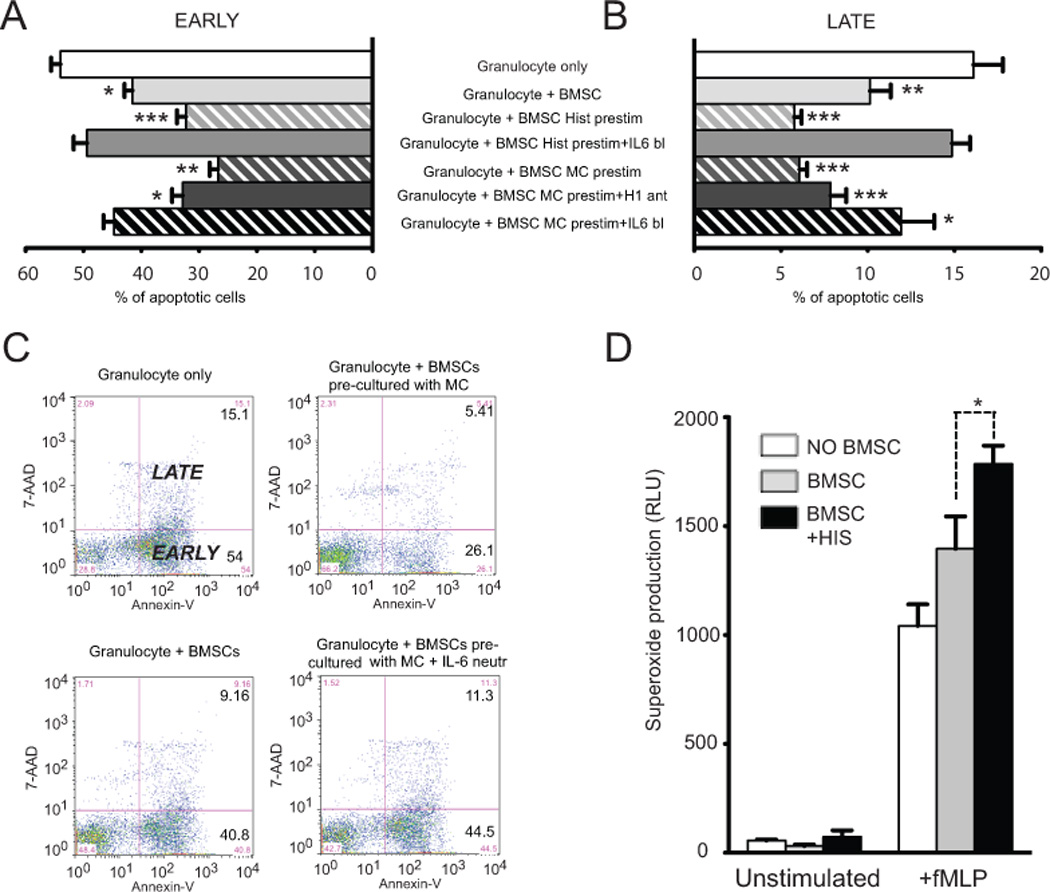
Histamine prestimulation increases the IL-6 driven antiapoptotic effect of BMSCs on peripherial blood derived granulocytes.
When placed in co-culture BMSCs effectively suppressed spontaneous apoptosis of neutrophils as measured by Annexin-V binding and concurrent 7-AAD staining using FACS (A-C). Histamine prestimuation of BMSCs was able to even further decrease the number of apoptotic PMNs. This potentiation of antiapoptotic function was eliminiated in the presence of neutralizing anti-IL-6 antibodies in the media. In another set of experiments instead of adding histamine itself we used degranulated human mast cells as a source of histamine to prestimulate the stromal cells. These pretreated BMSCs exhibited a significantly greater antiapoptotic effect as compared to histamine stimulation alone. Moreover this increased pro-survival phenotype was only partially suspended in the presence of H1 receptor blockade. IL-6 neutralization eliminated the anti-apoptotic effect. Neutrophil granulocytes significantly increased their fMLP induced superoxide production when they were co-cultured with BMSCs. Histamine prestimulation of BMSCs further increased the superoxide production of neutrophil granulocytes (D).
