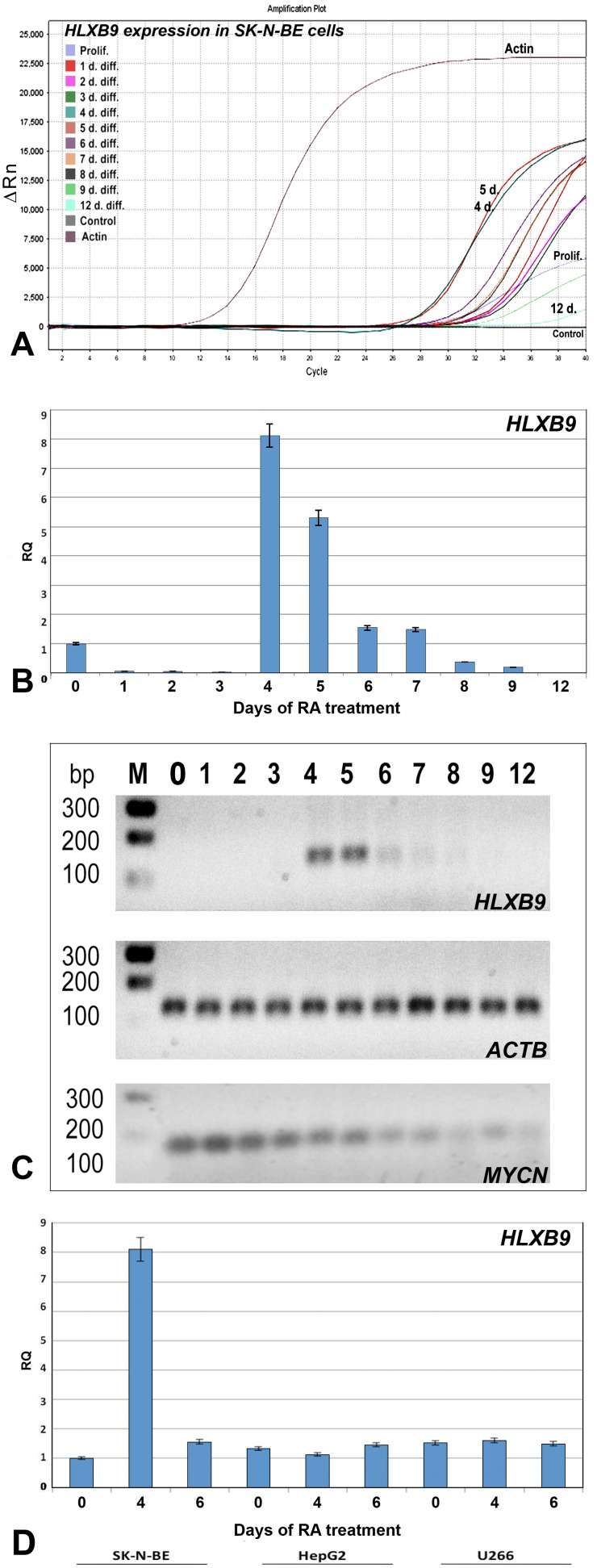
Figure 2. HLXB9 expression in SK-N-BE.
(A) Amplification plot of Real time PCR experiments. Data show HLXB9 expression in SK-N-BE cells at different days after retinoic acid treatment in comparison with expression of ACTB (Actin-B) used as a control. (B) Histogram generated with values of 2−ΔΔCt. Samples are on x-axis and fluorescence emission is on y-axis. The increase of HLXB9 expression in SK-N-BE cells is noted dramatically on the fourth and fifth day of differentiation. Subsequently, HLXB9 expression decreases until disappearing at day 12. (C) Electrophoresis of the Real time PCR fragments obtained with the specific primers for HLXB9 and for the control gene ACTB. Electrophoresis of MYCN Real time PCR fragments was also shown. In B, and C “0” indicates proliferating cells before treatment with retinoic acid. D) Histogram generated with values of 2−ΔΔCt. Samples are on x-axis and fluorescence emission is on y-axis. There isn’t a significant increase of HLXB9 gene expression in U266 and HepG2 cells, when cells are treated with retinoic acid. Data in the graphs B, and D are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM).