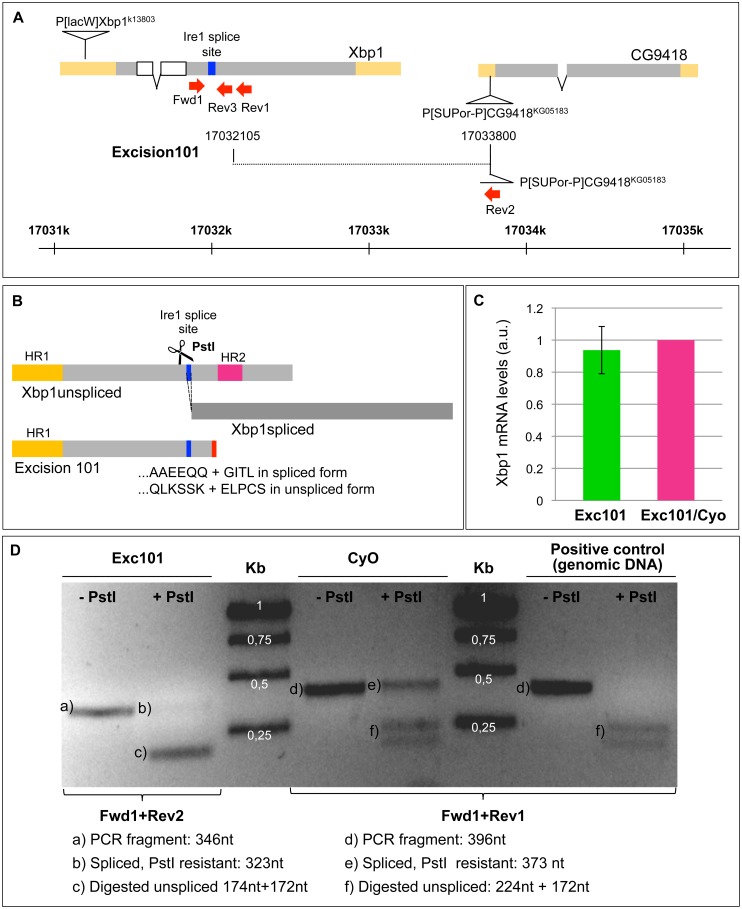
Figure 3. Excision101 originates a truncated Xbp1 mRNA that is spliced by Ire1.
(A) Schematic representation of genomic region around Xbp1, with the localization of Excision101 deletion and the PCR primers Fwd1, Rev1, Rev2 and Rev3. In Excision 101, the breakpoint in P{SUPor-P}CG9418KG05183 is 5′GAA TTA CCT TGT AGT TGA TAT TTG AGA T (following the leading strand of Xbp1). (B) Schematic representation of the Xbp1unspliced and Xbp1spliced proteins in “wild-type” and in Excision101. PstI has a cleavage site in the intron spliced by Ire1. HR1: hydrophobic region 1. HR2: hydrophobic region 2. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR for total Xbp1 mRNA levels in larvae homozygous for Excision101or heterozygous Excision101/CyO-GFP, using the primers for Xbp1, Fwd1 and Rev3. Control Excision101/Cyo is set as 1, with the homozygous Excision101 Xbp1 mRNA levels indicated as a mean +/− standard deviation (a.u. - arbitrary units). (D) Agarose gel electrophoresis of RT-PCR products specific for Excision101 or CyO control chromosome after digestion with PstI restriction enzyme. PCR product specific for the Xbp1unspliced form is cleaved by PstI, while Xbp1spliced form is resistant to PstI digestion (because the PstI is in the intron that is spliced by Ire1). A positive control using genomic DNA is fully digested by PstI.