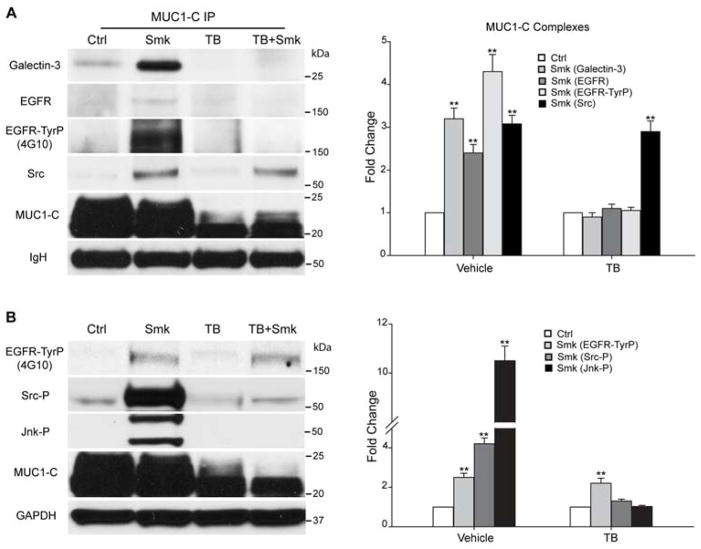
Figure 5.
Smoke-induced MUC1-C glycosylation modulates MUC1-C/galectin-3/EGFR complex formation and Src/Jnk/MUC1-C signaling downstream of EGFR in polarized HBE cells. (A–B) HBE cells were preincubated with TB or vehicle control (DMSO) overnight before treating with Smk or Ctrl medium for 4h in the presence of TB. (A) MUC1-C IP was analyzed with WB probed with galectin-3, EGFR, TyrP (4G10), Src and MUC1-C antibodies. The 175kDa bands recognized by 4G10 completely overlapped with EGFR. Equal loading was confirmed with IgH bands. Quantitation of MUC1-C bound galectin-3, EGFR, EGFR-TyrP and Src after smoke and/or TB exposure was normalized to untreated control (designated as 1-fold) and reported as mean ± SEM fold change. (B) WB probed with TyrP (4G10), Tyr416-phosphorylated Src (Src-P), Thr183/Tyr185-phosphorylated SAPK/Jnk (Jnk-P) and MUC1-C antibodies. The 175kDa bands recognized by 4G10 completely overlapped with EGFR. Equal loading was confirmed with GAPDH. Densitometric quantitation of EGFR-TyrP, Src-P and Jnk-P after smoke and/or TB treatment was normalized to untreated control (designated as 1-fold) and graphed as mean ± SEM fold change. **p < 0.01, Smk-treated cells versus untreated Ctrl.