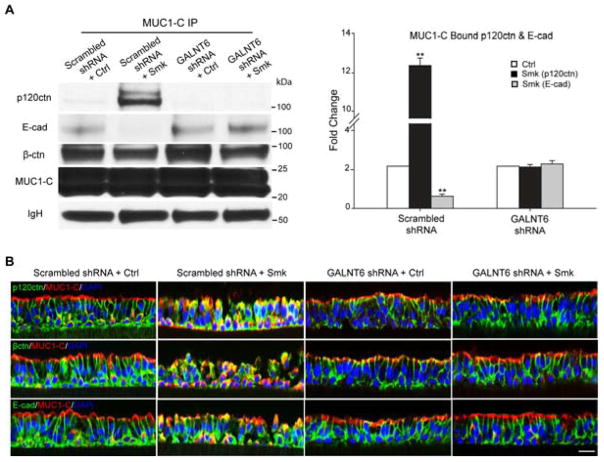
Figure 7.
Suppression of smoke-induced MUC1-N glycosylation abolished smoke-provoked MUC1-C/p120ctn interaction and E-cad loss in polarized HBE cells. (A–B) Polarized HBE cells were infected with 1*MOI of adenoviral scrambled shRNA or GALNT shRNA overnight and cultured for another 4 days before exposing to Ctrl or Smk medium for 4h. (A) The cell lysates were IP’d with anti-MUC1-C followed by WB probed with p120ctn, E-cad, β-ctn and MUC1-C antibodies. Equal loading was confirmed with IgH bands. Densitometric quantitation (mean ± SEM fold change, **p < 0.01) of MUC1-bound p120ctn (black columns) and E-cad (gray columns). (B) Immunofluorescent staining of polarized HBE cells exposed to scrambled shRNA/Ctrl, scrambled shRNA/Smk, GALNT6 shRNA/Ctrl and GALNT6 shRNA/Smk for p120ctn (green, top panels), β-ctn (green, middle panels), E-cad (lower panels) and MUC1-C (red, all panels), DAPI nuclear counterstain (blue). Scale bar represents 50μm.