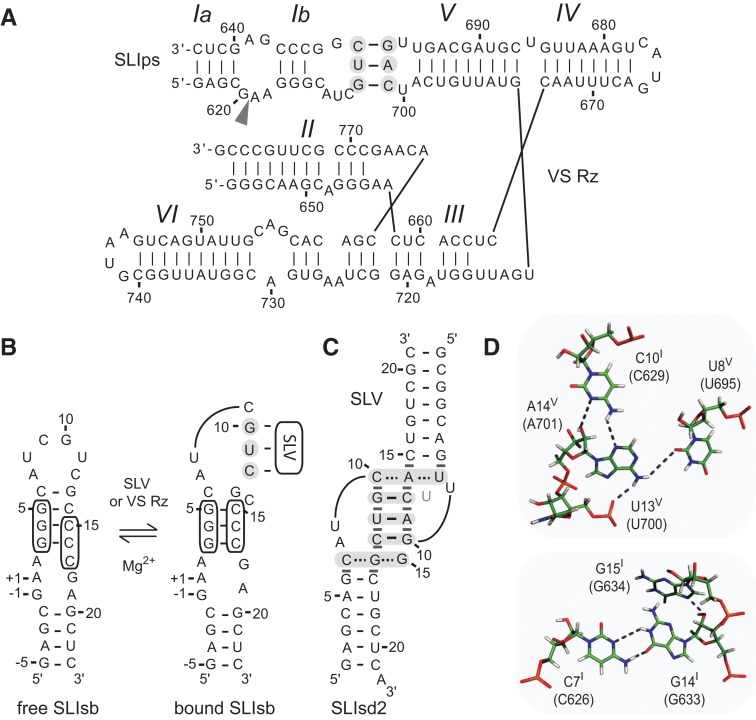
FIGURE 1.
Primary and secondary structures of the Neurospora VS ribozyme. (A) The catalytic domain of the VS ribozyme containing helical domains II-VI (VS Rz) and an SLI substrate (SLIps) containing stems Ia and Ib. The cleavage site is indicated by an arrowhead. The I/V kissing-loop interaction involves W-C base pairs (black lines) between shaded residues of SLI and SLV (Beattie et al. 1995; Rastogi et al. 1996). (B) Formation of the I/V kissing-loop is accompanied by a structural rearrangement of the SLI substrate from an unshifted (free) to a shifted (bound) conformation. The cleavage site is between residues −1 and +1 of SLIsb. (C,D) Structural characteristics of the I/V kissing-loop based on the NMR structure of the SLIds2/SLV complex (Bouchard and Legault 2014). In C, W-C and noncanonical base pairs are represented by solid and dashed lines, respectively, on the secondary structure of the complex, whereas stable base stacking at the kissing-loop junction is illustrated by gray rectangles. U13 is in gray to illustrate its extrusion from the loop V fold. In D, hydrogen bonds within the base triples of the minimized averaged structure are represented by dotted lines.