FIGURE 4.
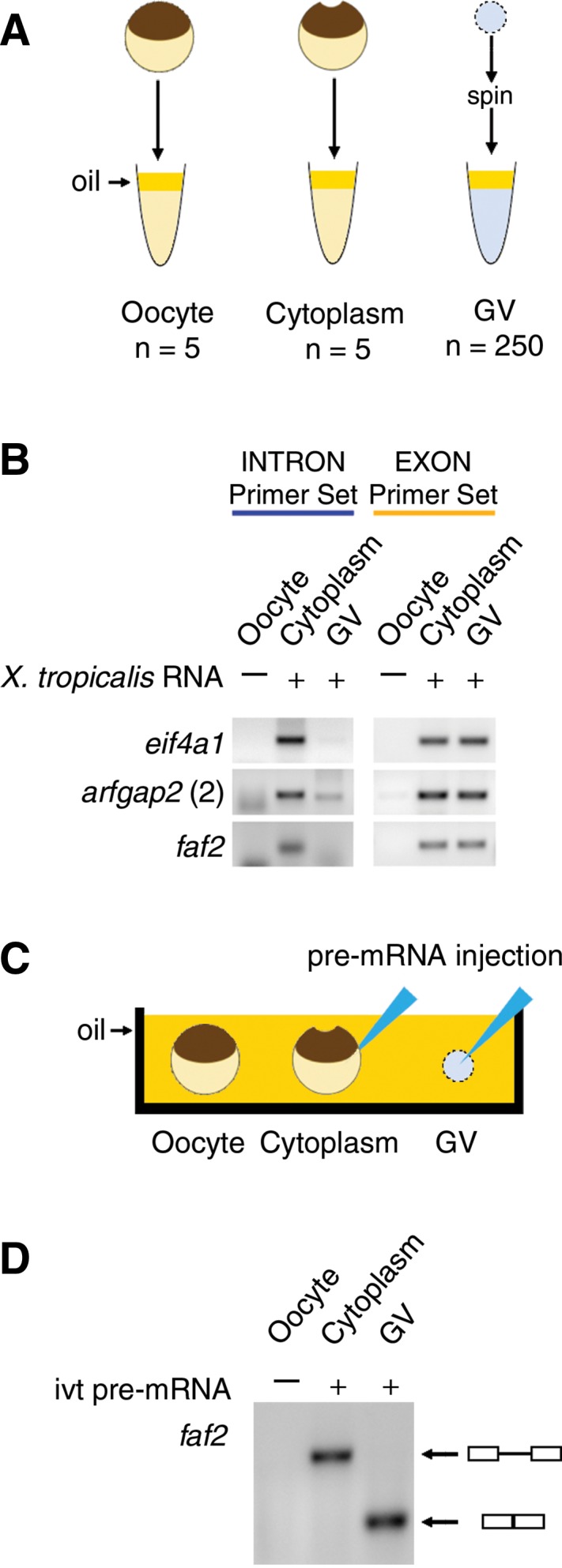
(A,B) The stability of X. tropicalis cytoplasmic RNA (1 µg) was tested by RT–PCR after incubation in X. laevis cytoplasmic or nuclear extracts. (A) Extracts of X. laevis whole oocytes, oocyte cytoplasm, and GVs were made under oil. (B) Cytoplasmic sisRNAs from X. tropicalis were degraded by a GV extract from X. laevis but not by a cytoplasmic extract (intron primer set, blue). Exonic sequences from X. tropicalis were stable for 2 h in both GV and cytoplasmic extracts (exon primer set, yellow). (C,D) Splicing activity was tested by injecting an in vitro-transcribed X. tropicalis pre-mRNA construct into the cytoplasm or GV of an X. laevis oocyte. (C) Injection of the construct was carried out under mineral oil. (D) After incubation for 2 h, an RT–PCR reaction was carried out on the cytoplasm and GV using primers from the ends of the construct. The products were run on an agarose gel and stained. Splicing occurred only in the GV, as shown by the expected smaller size of the RT–PCR product.
