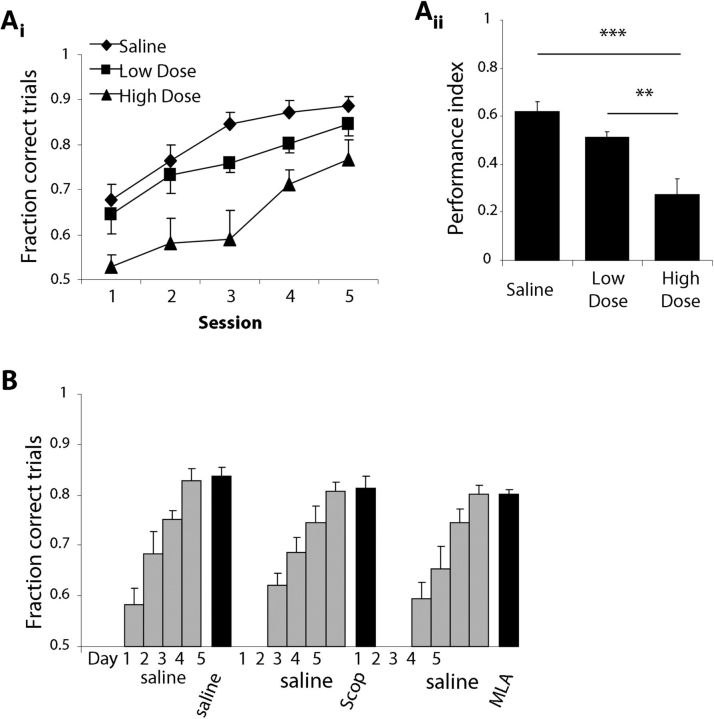
Figure 8.
Behavioral control experiments. A, Dose–response curve for dissimilar odor sets. Ai, Average performance (±SEM) as a function of test session for rats performing the novel odor acquisition task using dissimilar odor sets (n = 6 odor sets) and receiving either a high dosage of cholinergic antagonists (scopolamine, 22 mm; MLA, 19 mm), a low dosage at one-fifth the original concentration (scopolamine, 4.4 mm; MLA, 3.6 mm), or saline infusions. Aii, PI for each of the drug treatment groups. **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.001. B, Control for impairment of general odor processing and perception. The graph shows the average performance as a function of daily sessions for three experimental groups. All groups received saline infusions for the first 4 d of training, followed by a fifth day in which they received either saline, scopolamine (22 mm), or MLA (19 mm) infusions. These graphs indicate that once an odor discrimination task has been acquired, manipulation of bulbar cholinergic modulation does not affect discrimination performance.