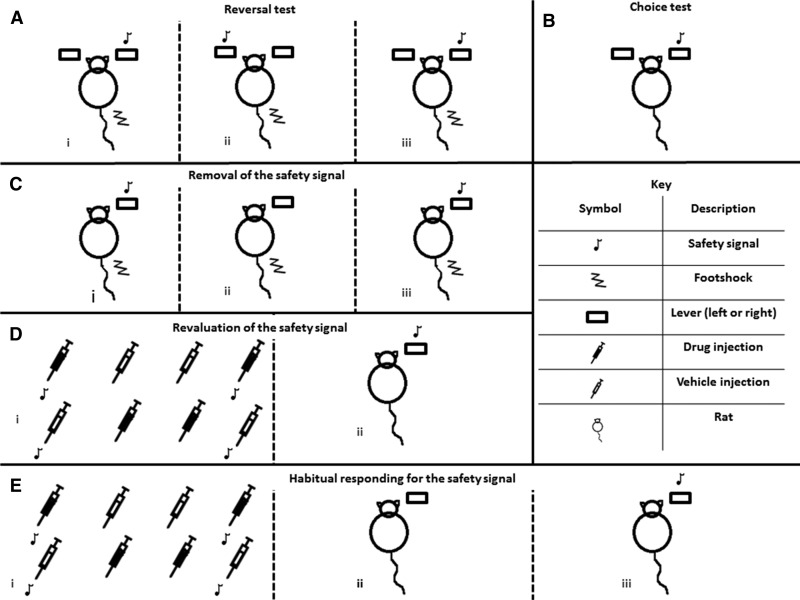
Figure 6.
Schematics of experimental procedures. (A) Experiment 1: reversal test, two levers are presented which both avoid shock but only one produces the safety signal (i) for the first three days (Phase 1) this is presented following responding on the same lever (either right or left counterbalanced across subjects), (ii) for the next three days the safety signal is presented following responding on the alternate lever to that of the first three days (Phase 2), (iii) the safety signal is presented following responding on the same lever as used in the first three days for three more days (Phase 3). (B) Two-lever choice test where one lever produces the safety signal but no shocks are presented in the session. (C) Experiment 2: removal of the safety signal on avoidance responding, (i) baseline session, responses avoid shock and produce the safety signal, (ii) responses avoid shock but do not produce the safety signal, (iii) responses avoid shock and produce the safety signal. (D) Experiment 3: revaluation of the safety signal, (i) revaluation procedure; (top line) the paired group; (bottom line) the unpaired group, (ii) drug-free test session where responses on a single lever produce the revalued safety signal, no shocks are presented during the revaluation and extinction test sessions. (E) Experiment 4: habitual avoidance behavior test, (i) revaluation procedure; (top line) the paired group; (bottom line) the unpaired group, (ii) drug-free test session where responses on a single lever do not produce the revalued safety signal, and (iii) reinforced test where responses on a lever produce the revalued safety signal; no shocks are presented during revaluation or test sessions.