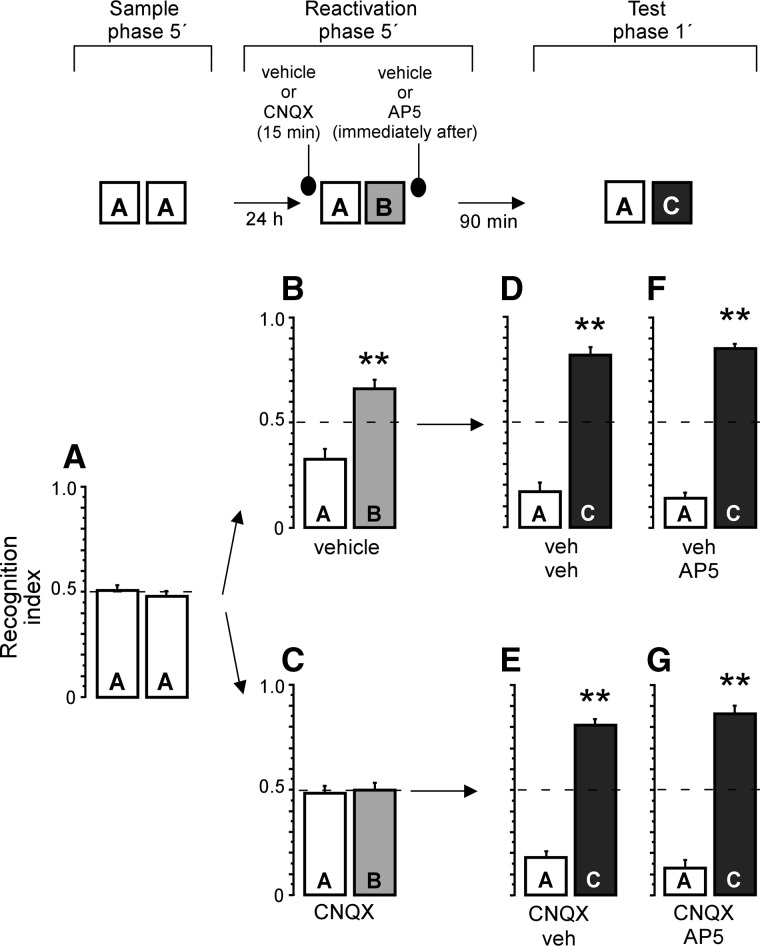
Figure 2.
NMDA and AMPA receptor antagonists did not disrupt short-term object recognition memory. Recognition index on sample phase, when rats were exposed to two identical objects (A). Animals infused with vehicle but not CNQX showed preference for the novel object (B,C) on the reactivation trial. (D) veh/veh group showed preference for the novel object when tested. Similarly, CNQX-infused group (E) showed preference for the novel object when tested 90 min after retrieval, revealing that the effect of CNQX was transient. (F,G) AP5 infusions did not affect memory tested in the short term, whether or not memory retrieval was blocked. (**) P < 0.01 vs. recognition index = 0.5.