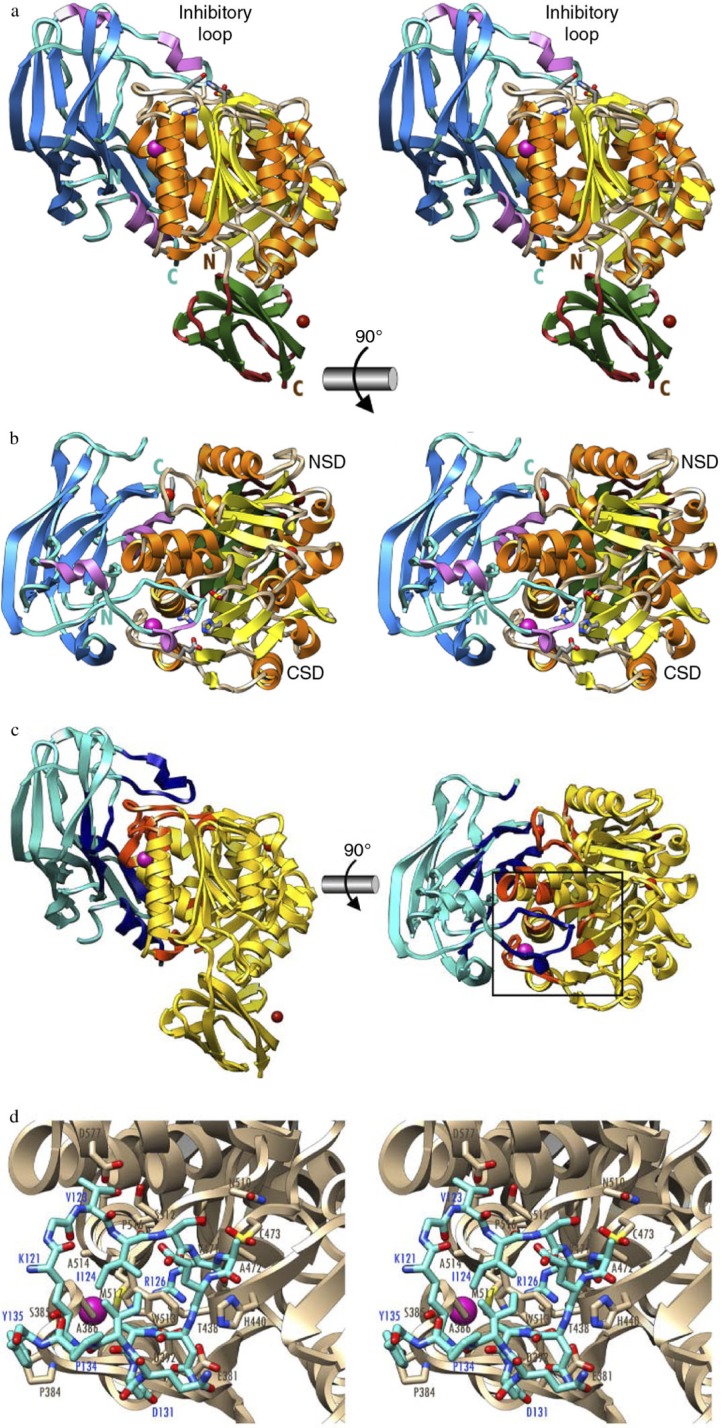
Fig. 1.
The structure of the zymogenic complex of the N-terminal prodomain (NPD) with mature RgpB. (a) Ribbon-type plot in wall-eyed stereo image of the complex between the RgpB PD (in blue/magenta) and the mature RgpB moiety in front view. The latter consists of domains CD (in yellow/orange) and IgSF (in green/brown). The three calcium ions and the barium ions are depicted as red and magenta spheres, respectively. The inhibitory loop and the respective N and C termini are labeled, in turquoise for PD and in brown for CD +IgSF. Arg126 from the PD inhibitory loop and the active-site residues of CD (Cys473, His440, and Glu381) are further shown as sticks for reference of the active site. (b) Orthogonal view of a showing the CD in standard orientation, that is, with the view into the active-site cleft, which runs horizontally from left (non-primed side) to right (primed side). (c) View of the complex in the orientations of a (left) and b (right) showing the regions of the PD and CD engaged in binding in dark blue and orange, respectively. The rest of each molecule is shown in turquoise and yellow, respectively. (d) Close-up view in wall-eyed stereo image of the area around the inhibitory loop delimited by a black rectangle in c. The CD moiety is shown as a tan ribbon, and selected residues are labeled and shown for their side chains as sticks with tan carbons. The inhibitory loop (Lys121–Tyr135) is shown as a stick model with carbons in turquoise. Selected residues are also labeled. The barium ion of the CD is depicted as a magenta sphere. Note that the catalytic cysteine, Cys473, is oxidized to 3-sulfino-L-alanine (residue name CSD). Obtained from de Diego et al. (12).