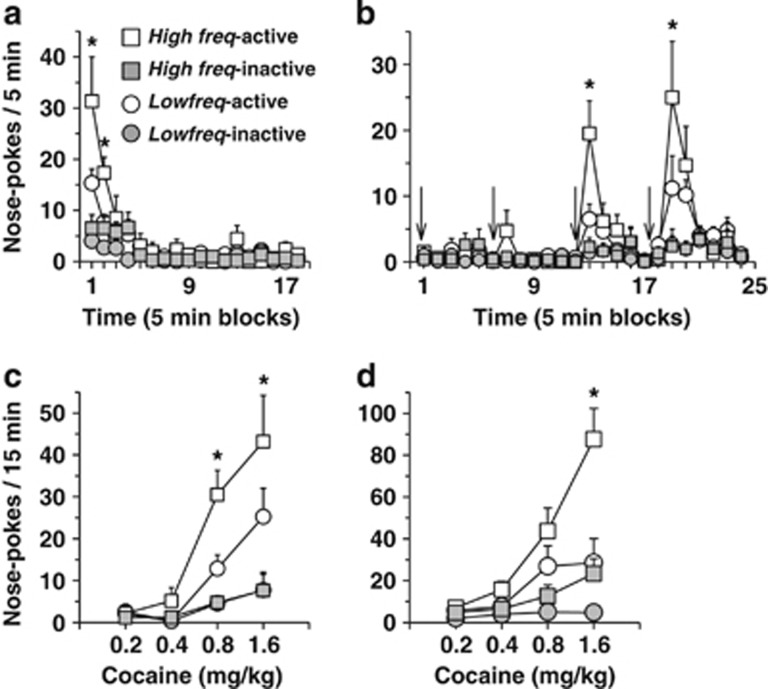
Figure 3.
Reinstatement of cocaine self-administration behavior in High (High freq) and Low frequency rats (Low freq). The session lasted 210 min (90 min extinction+120 min of cocaine-induced reinstatement). (a–c) Experiment 1. (a) Time course of active and inactive nose-pokes during the 90 min period of extinction. Active nose-pokes were higher in the High frequency rats, over the first 10 min. Behavior was fully extinguished in both groups when the first cocaine dose was infused. (b) Time course of active nose-pokes following four non-contingent infusions (one every 30 min) of increasing doses of cocaine (time of infusions is indicated by a black arrow). Cocaine induced a dose-dependent increase of active response, an effect that was higher in High frequency rats. (c) Dose-response of reinstatement. Total active and inactive responses over the first 15 min following each cocaine infusion are represented (n=12 to 13 per group). *p<0.05 as compared with Low freq rats. (d) Experiment 2: total active and inactive responses over the first fifteen minutes following each cocaine infusion are represented. Rats had been administered with virus and optical fibers into the PL before self-administration training. As for Experiment 1, High frequency rats showed higher cocaine-induced reinstatement than Low frequency rats (n=17 High freq (EYFP & ArchT) and n=11 Low freq (ChR2)). *p<0.05 as compared with Low freq rats. Data are expressed as mean±SEM.