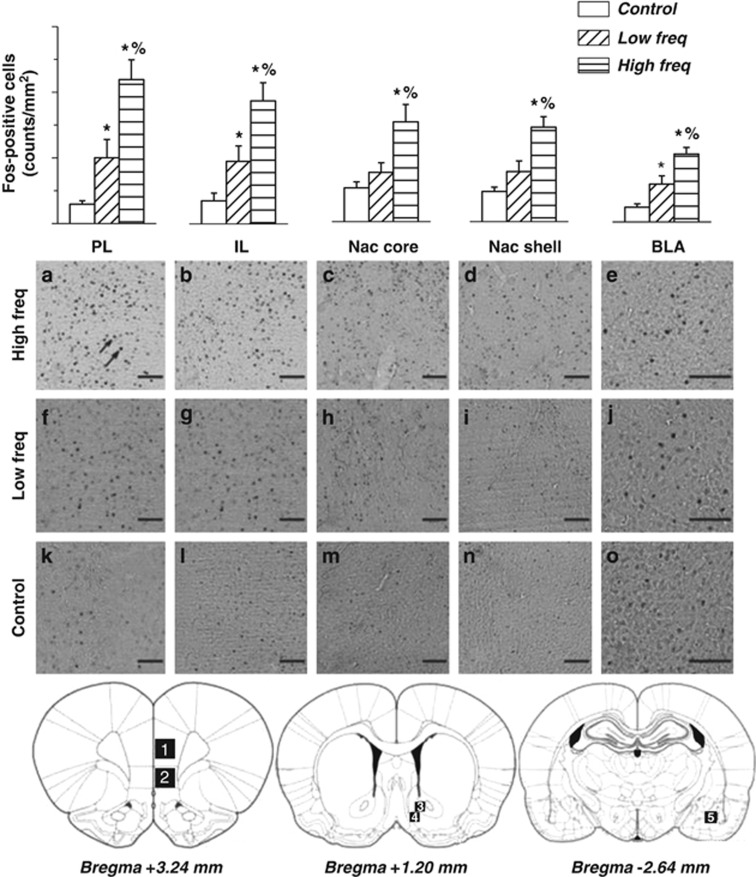
Figure 4.
In the upper part, mean number of c-Fos-positive cells/mm2 in PL, IL, NAc Core, NAc Shell, and BLA in High (High freq) and Low frequency (Low freq) rats. The three groups significantly differed for c-Fos expression in the five structures of interest. In the prelimbic cortex (PL), infralimbic cortex, (IL) and basolateral amygdala (BLA), cocaine self-administration increased c-Fos expression, but High frequency rats showed higher c-Fos expression than Low frequency rats. In the nucleus accumbens core (NAc core) and nucleus accumbens shell (NAc shell), High frequency was specifically associated with increased c-Fos expression, as Low frequency rats did not differ from Control rats. Data are expressed as mean±SEM (n=4–6 per group). *: significant as compared with Control, %: significant as compared with Low frequency rats. In the medium part, representative pictures of c-Fos staining in the five structures of interest for the three experimental groups (a–e: High frequency, f–j: Low frequency, and k–o: Control). In the bottom part, pictures are schematic representations of coronal sections of the rat brain taken at 3.24, 1.20, and −2.64 mm from the bregma (Paxinos and Watson, 2005). Numbers in the sections represent the regions analyzed for c-Fos: (1) PL; (2) IL; (3) NAc core; (4) NAc shell; (5) BLA. All images were taken at × 10 magnification. Scale bar is equal to 100 μm. Visible c-Fos protein expression was manifested as dark ovals (highlighted by arrows).