Extended Data Figure 3. Identification of Cu-binding mutants of MEK1 that reduce ERK1/2 phosphorylation.
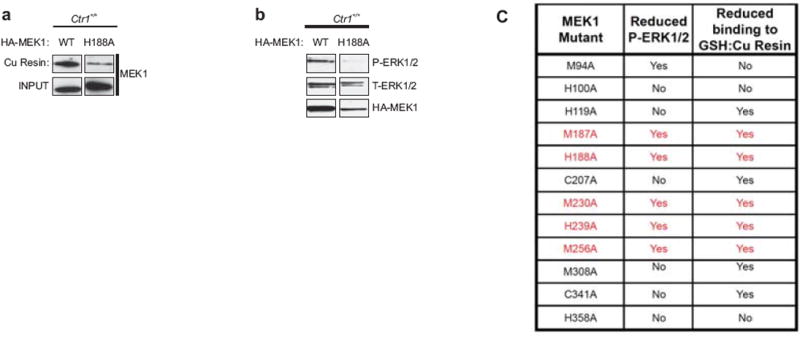
a, Immunoblot detection of the amount of HA-tagged wild-type (WT) MEK1 and an example of one MEK1 mutant tested (H188A) that bound to a Cu-charged resin. Input serves as a loading control. b, Immunoblot detection of the amount of phosphorylated (P) and/or total (T) ERK1/2 or HA-MEK1 protein in immortalized Ctr1+/+ MEFs stably expressing HA-tagged wild-type (WT) MEK1 or an example of one MEK1 mutant tested (H188A). c, Summary of whether the indicated MEK1 point mutants did (YES) or did not (NO) exhibit a reduction in binding to the Cu-charged resin or show a reduction in the levels of phosphorylated (P) ERK1/2 when stably expressed in immortalized Ctr1+/+ MEFs. Gel images are representative of two replicates.
