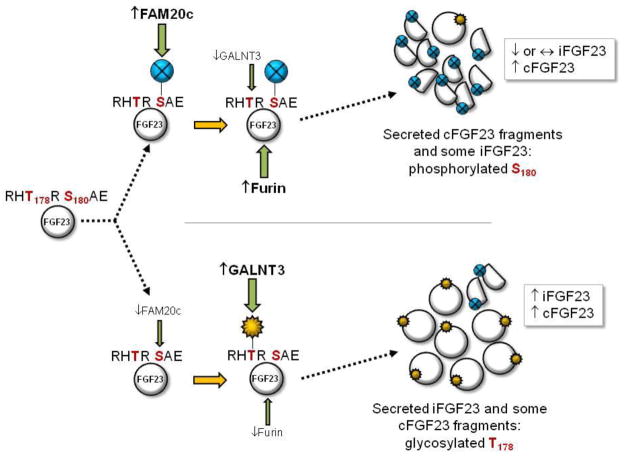
Figure 2. Model for dynamic control of iFGF23:cFGF23 ratios.
The study of diseases involving altered iFGF23:cFGF23 ratios, including ADHR and Raine’s syndrome, has introduced a model for dynamic FGF23 regulation. FGF23 protein (far left) carries an RHT178R-S180AE motif that comprises an ‘RXXR/S’ subtilisin-like proprotein convertase (SPC) site. (Upper) When FAM20c activity/expression is increased, S180 is phosphorylated and GALNT3 O-glycosylation of T178 may be inhibited making iFGF23 a furin substrate, thus levels of secreted iFGF23 can remain constant (or potentially decrease) with a corresponding increase in cFGF23 proteolytic fragments. (Lower) When FAM20c activity/expression is reduced, GALNT3 O-glycosylates FGF23 T178, which prevents furin cleavage resulting in increased secretion of iFGF23.