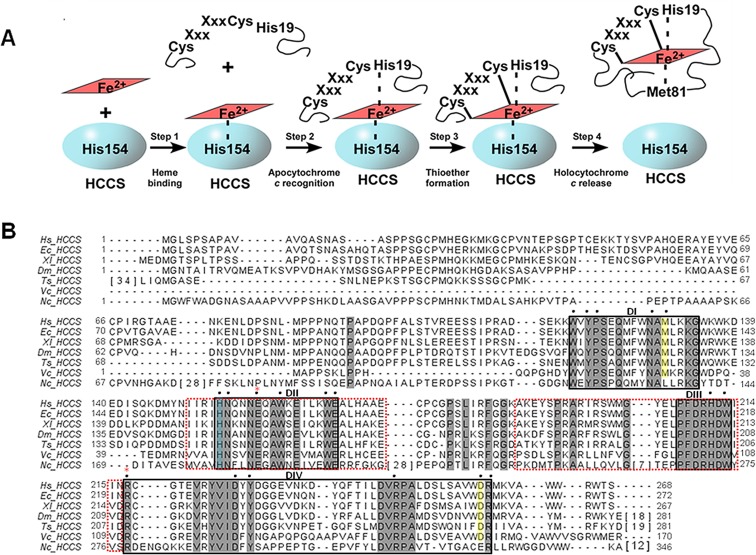
Figure 1.
HCCS model for cytochrome c assembly and primary sequence. (A) Model of HCCS-mediated cytochrome c assembly adapted from ref (20). (B) ClustalW-generated alignment of HCCS homologues from various eukaryotic organisms. Sequences with extensive gaps in conservation were condensed, with the number of intervening residues enclosed by brackets. Residues shaded in gray are conserved across diverse phyla. Residues shaded in yellow are conserved in HCCS homologues from animals. Putative functional and/or structural domains are indicated (DI, DII, DIII, and DIV) and are enclosed by black boxes. Domains that mediate mitochondrial import are enclosed by red-dashed boxes. Black dots indicate residues that were substituted either previously (H154 and H211 in ref (20)) or for the present study. The His154 ligand to heme iron is shaded blue. Red asterisks indicate residues that undergo mutation in patients with MLS (E159 and R217). Hs, Homo sapien (UniProt P53701); Ec, Equus caballus (UniProt F6YF82); Xl, Xenopus laevis (UniProt Q6DOG6); Dm, Drosophila melanogaster (UniProt Q9VD55); Ts, Trichinella spiralis (UniProt E5SBT9); Vc, Volvox carteri (UniProt D8U027); Nc, Neurosporo crassa (UniProt P14187).