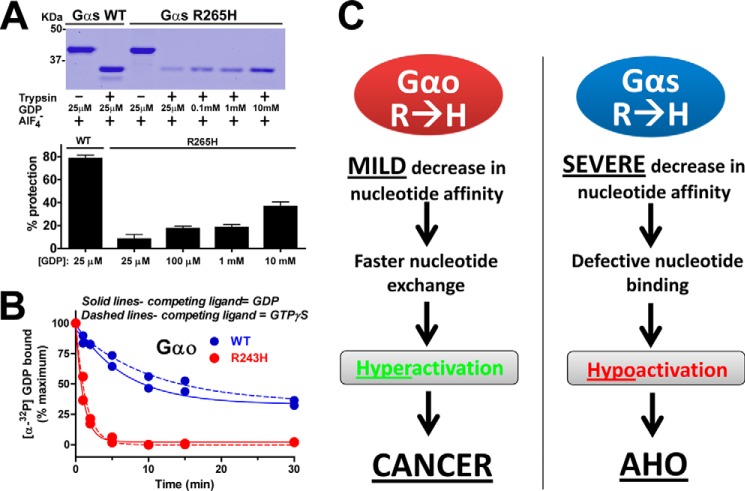
FIGURE 4.
GDP binding affinity of Gαs R265H is severely impaired whereas it is mildly reduced for Gαo R243H. A, Gαs R265H is partially protected from trypsin digestion in the presence of AlF4− only at high, supraphysiological concentrations of GDP. His-Gαs WT or R265H were incubated in the presence of 30 μm AlCl3, NaF 10 mm, and the indicated concentrations of GDP before treatment with trypsin as described in “Experimental Procedures.” One representative experiment is shown on the top, and a graph with a graph with the mean ± S.D. of two independent experiments is shown on the bottom. B, mutation of Arg-243 to His accelerates the rate of [α-32P]GDP release from Gαo. [α-32P]GDP-loaded Gαo WT (blue) or Gαo R243H (red) was challenged with excess unlabeled GDP (solid lines) or GTPγS (dashed lines) and [α-32P]GDP remaining bound to Gαo was measured at different time points as described in “Experimental Procedures.” One experiment representative of three is shown. C, schematic diagram summarizing the proposed molecular mechanism underlying the involvement of Gαo R243H and Gαs R265H in disease.