FIGURE 5.
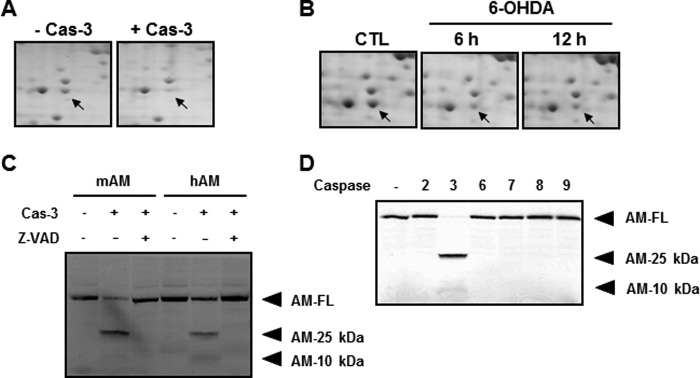
Confirmation of anamorsin as a novel caspase-3 substrate. A, MN9D cellular lysates (1.5 mg) were processed for two-dimensional electrophoresis following incubation with or without 25 μg of recombinant human caspase-3 (Cas-3). Arrows indicate the Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250-stained protein spot, the level of which decreased in the presence of casapse-3 compared with untreated control. Mass spectrometry indicates that this protein spot is anamorsin. B, MN9D cells were treated with or without a prototypic apoptotic inducer, 100 μm 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) for the indicated time periods. Total cellular lysates were processed for two-dimensional electrophoresis, and the separated protein spots on the gel were stained with 0.1% Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250. A close-up view of the same gel position as in A is demonstrated for each time period. Arrows indicate the expression level of anamorsin following 6-hydroxydopamine treatment or sham treatment (CTL). C, in vitro caspase-3 cleavage assay confirmed that the metabolically labeled mouse (mAM) and human anamorsin (hAM) were cleaved by 50 ng of caspase-3. Caspase-3-meidated cleavage of full-length anamorsin (AM-FL) resulted in the generation of two cryptic fragments with molecular sizes of 25 (AM-25 kDa) and 10 kDa (AM-10 kDa). This cleavage was blocked in the presence of 100 μm Z-VAD-fmk. D, specificity of caspase-3-mediated cleavage of anamorsin was confirmed by an in vitro caspase cleavage assay. Fifty nanograms of recombinant human caspase-2, -3, -6, -7, -8, and -9 were used for the reaction.
