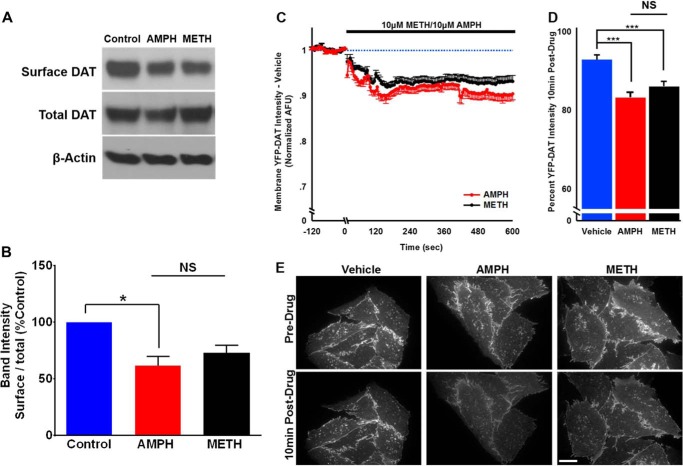
FIGURE 10.
Amphetamine-induced reduction in surface DAT levels was not different from methamphetamine. FLAG-DAT HEK cells were treated with amphetamine (10 μm) or methamphetamine (10 μm) for 10 min followed by treatment with sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin to detected surface DAT. A, representative immunoblots showing surface DAT, total DAT, and the loading control, β-actin. B, the bar graph shows after amphetamine treatment there was a significant reduction in the surface DAT compared with the control, whereas after 10 min of methamphetamine treatment surface DAT density was not significantly (NS) different from control or amphetamine. C, plot of membrane YFP-DAT intensity (arbitrary fluorescent units (AFU)) after exposure to amphetamine (10 μm) or methamphetamine (10 μm) normalized to the average intensity for each cell during the 15 s before solution change. The normalized response to vehicle (external solution) has been accounted for in the normalized values, correcting for fluorophore bleaching. D, the bar graph shows average normalized intensity after 10min of drug application. Both psychostimulants similarly and significantly internalized the dopamine transporter (***, p < 0.001; *, p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test). E, representative images showing amphetamine- and methamphetamine-induced reduction in the surface YFP-DAT intensity.