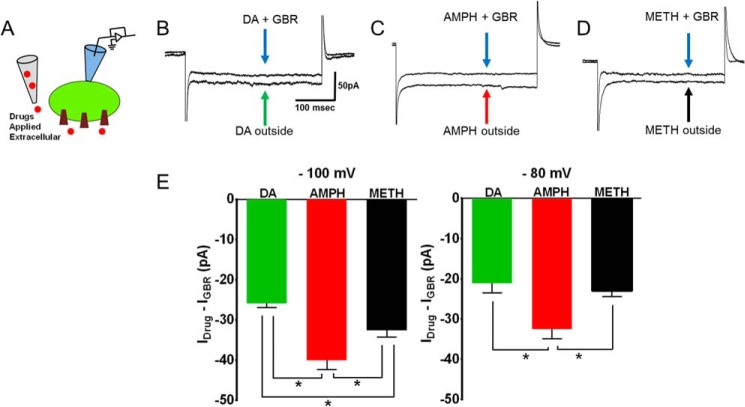
FIGURE 5.
Methamphetamine elicits smaller DAT-mediated inward current compared with amphetamine. A, schematic depicts the experimental configuration. The DAT-mediated inward current was measured when drugs are applied extracellularly. The substrate-induced, DAT-mediated current is defined as the GBR12935-subtracted current. The DAT-mediated, amphetamine- or methamphetamine-induced current was measured when the cells were voltage-clamped in whole-cell configuration. B–D, representative traces at −100 mV. E, the bar graph shows the average DAT-mediated current after bath application of dopamine (10 μm; n = 6), methamphetamine (10 μm; n = 6), and amphetamine (10 μm; n = 6) at −100 mV and −80 mV. The amphetamine-induced, DAT-mediated inward currents were significantly larger than methamphetamine-induced or dopamine-induced inward currents (*, p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test).