FIGURE 9.
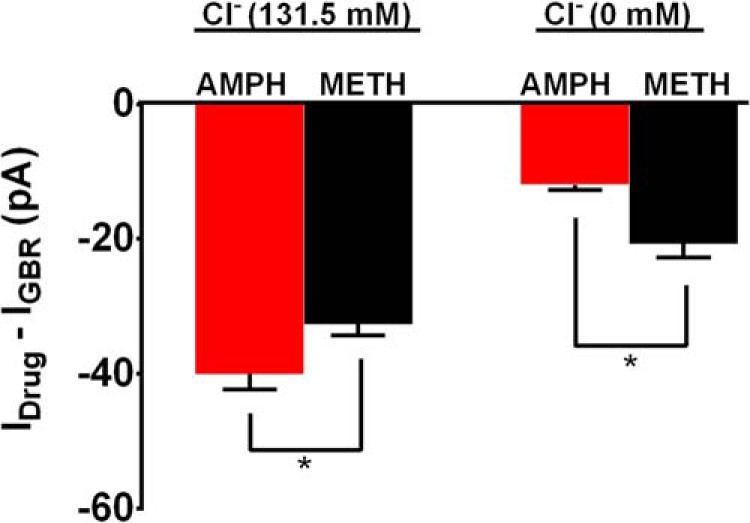
Side by side comparison of the effects of amphetamine versus methamphetamine-induced DAT-mediated inward currents. The bar graph shows a side by side comparison of the effects of amphetamine versus methamphetamine-induced DAT-mediated inward currents at (−100 mV holding potential) at two different concentrations of extracellular chloride ions (Cl−). We observed that at 0 mm Cl− ion concentration the inward current induced by amphetamine was significantly blocked and to a higher extent compared with methamphetamine, whereas at 131.5 mm extracellular Cl− ion concentration amphetamine produced significantly higher inward current compared with methamphetamine.
