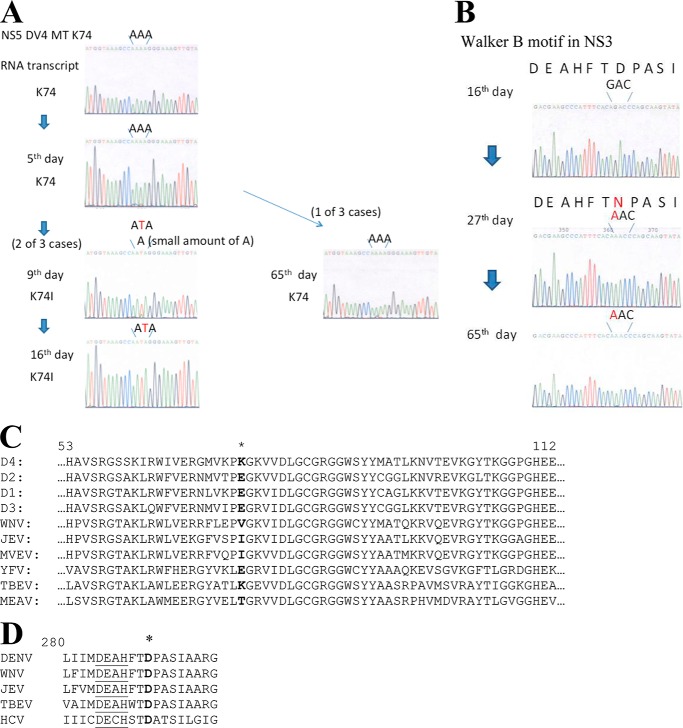
FIGURE 2.
Sequence analysis of the RNA transcript before and after electroporation into BHK-21 cells on the indicated days. A, the NS5 D4MT/D2POL chimeric RNA was synthesized by in vitro transcription and transfected into BHK-21 cells by electroporation as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Sequence analysis of the region of interest in the vicinity of Lys74 in the D4MT domain is shown in the original RNA before electroporation and RNA isolated from supernatants (virions released into the medium) on days 5, 9, 16, and 65. In two of three independent experiments, Lys74 was mutated to Ile on day 9. In the third experiment, Lys74 was stable up to day 65 at this position. B, alignment of the amino acid sequences surrounding Lys74 (aa 53–112) in the N-terminal regions of different flavivirus NS5s. The adaptive mutation, K74I, in the NS5 D4MT/D2POL chimeric RNA was identified after serial passages in BHK-21 cells. The location of Lys74 is indicated in boldface type with an asterisk in B. C, in the third independent experiment, the Lys74 position was retained in NS5, but sequence analysis of the entire genome showed that the D290N mutation in D2 NS3 occurred on day 27, which was retained at least up to day 65. D, alignment of the amino acid sequences surrounding the Walker B motif of flavivirus NS3. The WT NS3 amino acid sequence from 280 to 298 is shown. The conserved Asp at position 290 indicated in boldface type with an asterisk is substituted by Asn in the NS5 D4MT/D2POL chimeric virus on day 27. WNV, West Nile virus; JEV, Japanese encephalitis virus; MVEV, Murray Valley encephalitis virus; YFV, yellow fever virus; TBEV, tick-borne encephalitis virus; MEAV, Meaban virus.