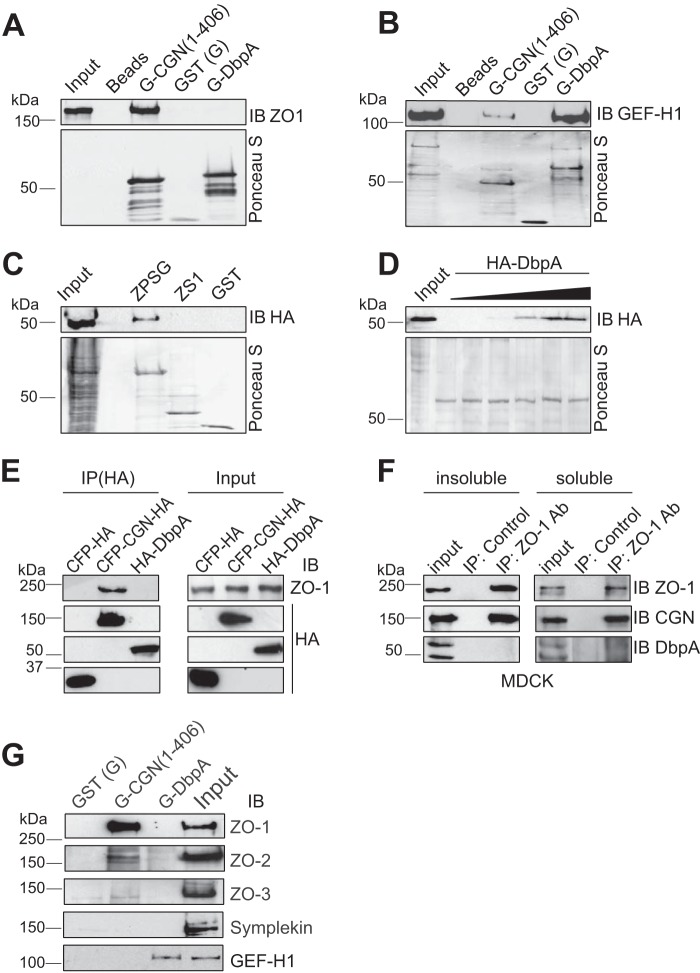
FIGURE 5.
Interaction of DbpA with ZO proteins. A and B, immunoblot (IB) analysis of GST pulldowns of either full-length recombinant ZO-1 (A) or GEF-H1 (B) produced in baculovirus-infected insect cells (input) using either Sepharose beads (Beads, negative control), or beads linked to GST (G) fused to the head region of cingulin (G-CGN(1–406)), or GST alone (GST), or GST fused to full-length DbpA (G-DbpA). The bottom panels in each image show Ponceau-S staining of the recombinant proteins used as baits in the pulldown assay. C, immunoblot analysis of GST pulldowns from lysates of HEK293 cells expressing HA-tagged DbpA, using as bait GST fused to the PDZ3/SH3/GUK domain of ZO-1 (ZPSG), GST fused to the SH3 domain (ZS1) or GST alone. D, saturation curve for the binding between ZPSG and HA-DbpA, using a fixed amount of bait, and increasing amounts of DbpA prey. E and F, immunoblot analysis (using either anti-ZO-1 antibodies or anti-HA antibodies) of: E, HA immunoprecipitates (IP) from lysates of HEK293 cells expressing myc-tagged-ZO-1 together with either HA-tagged CFP (negative control) or HA-tagged cingulin (positive control) of HA-tagged DbpA, and F, cytoskeleton-insoluble and -soluble fractions from MDCK cells (endogenous proteins), immunoprecipitated with either control or anti-ZO-1 antibodies. G, immunoblot analysis, using antibodies against ZO-1, ZO-2, ZO-3, symplekin, and GEF-H1, of MDCK lysates after pulldown using beads incubated with GST fused to the CGN head domain (G-CGN(1–406)), GST alone (G), or GST-DbpA (G-DbpA). Numbers on the left indicate the migration of pre-stained markers of known size (kDa).