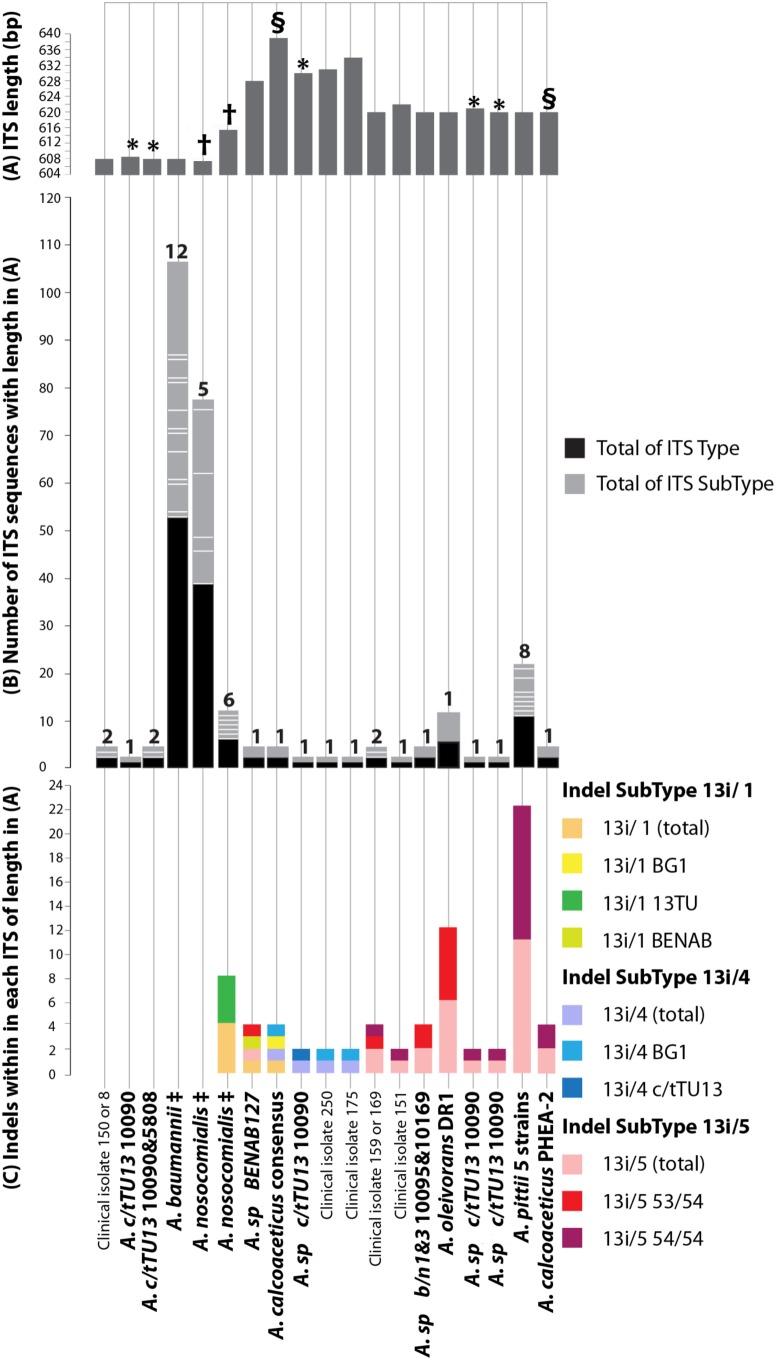
Figure 1. Sequence properties of ITS Acinetobacter Acb member strain sequences with one or more distinctive properties.
ITS-Type, ITS-Subtype, Indel Subtype and Indel Sequence Subtype defined in Results. ITS sequences were plotted with species on y-axis with established species in bold and collection C isolates in regular type. Figure 1A shows their individual ITS sequence lengths, Figure 1B the number of ITS sequences of a distinctive length (black) or sequence (grey) and Fig. 1C the number of indels (see Results) within each ITS of a distinctive length. The Acb species and strains associated with each ITS sequence length, number, sequence and indel type are given below. On x-axis: (A) ITS-lengths (named ‘Type’ and symbols refer to: * A. c/tTU13; § A. calcoaceticus; † A. nosocomialis); (B) Number of ITS-Types and -SubTypes (ITS copies of same sequence lengths but different sequences). Black/grey bars (parallel to green bar in A) show 40 ITS Types and 5 SubTypes of A. nosocomialis 607 bp ITS; black and grey bars (parallel to purple bar in A) show 5 ITS Types and 5 SubTypes of A. nosocomialis 615 bp ITS; white lines show number of each SubType; (C) Number of specific Indel Subtypes and Sequence Subtypes as totals for each strain are shown by coloured bars. See Fig. 3 for sequences; each indel subtype name refers to strains with 13i/1 and 13i/4 indels. 13i/5 53/54 refers to homology in 53/54 nucleotides, while 13i/5 54/54 indicates sequence homology for all 54 nucleotides). ‡ Refers to A. baumannii strains in Table 1 and M&M, isolates 147–8, 7; A. nosocomialis 607/8 bp, 00574, v104-2, DR25612/96, DR3226/96, DM18619/96, 74510, AB22222, isolates 149, 153–6, 160, 163–8, 170–1, 176–8, 180–1, 248–9, 251–7; A. nosocomialis 615/6 bp, TG21145, BCRC15417T, AB22222, NCTC8102, isolate 157; A. pittii, DSM9306, D499, DSM21653, TG6411, SH024. * Property defined as: ‘Species’, ‘Strain’, ‘Type’, ‘SubType’, ‘Indel’, ‘Indel sequence subtype’, ‘rrn allele name’. ¶ With ITS sequence Types of different lengths (608 to 638 bp), depending on their length and/or sequence, between 90–100% of the sequence is homologous, allowing for precise alignment. The alignment program introduces indels into regions not homologous with high numbers of other sequences in these regions, depending on ITS sequence Type length. Details in Gürtler & Grando [42] and Gürtler et al [43].