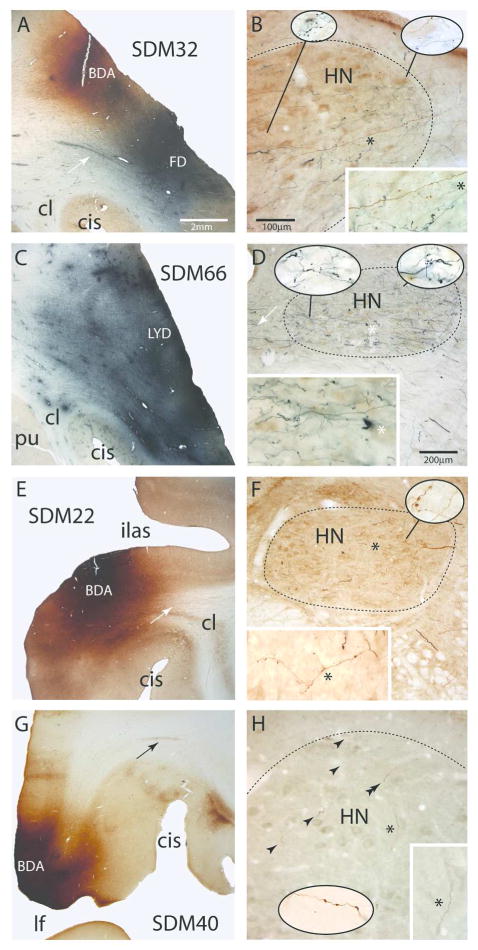
Figure 4.
Plate of photomicrographs showing representative examples of cortical injection sites on the lateral wall of the monkey (Macaca mulatta) cerebral hemisphere (left panels, A,C,E,G) giving rise to terminal labeling in the hypoglossal nucleus (HN) of cranial nerve XII (right panels, B,D,F,H). A) Coronal section showing the dorsally located BDA injection site (brown) and ventrally located FD injection site (blue) in the M1 orofacial representation in case SDM32. The white arrow denotes a well-defined bundle of FD labeled axons emerging from the cortical FD injection site. The micron bar is also applicable to panels C,E and G. B) Photomicrographic image of a horizontal section showing BDA (brown) and FD (blue) labeled fibers and terminals in the ipsilateral hypoglossal nucleus (HN) in case SDM32. The micron bar also applies to the main panel in plate H. Note the extensive terminal labeling throughout the nucleus and dense distribution of fibers coursing in the ventrolateral region toward more medially located regions of the nucleus. The asterisk in the main panel denotes the location of the higher powered inset in the bottom right hand corner of the panel. The pull-out spheres show higher power (100x) images from selected regions of the nucleus. C) Coronal section showing the LYD injection site (blue) in the ventral region of the M1 orofacial representation in case SDM66. D) Photomicrographic image of a horizontal section illustrating FD (blue) labeled fibers and terminals in the contralateral hypoglossal nucleus in case SDM66. Heavy terminal labeling is notable throughout the nucleus and the dense distribution of fibers can be seen coursing across in the lateral region of the nucleus toward more medially located targets. The white arrows show fibers that decussate across the midline at the level of the HN. The asterisk in the main panel denotes the location of the higher powered inset in the bottom right hand corner of the panel. The pull-out spheres show higher power (100x) images from selected regions of the nucleus. The micron bar applies to the main panel in plate F. E) Coronal section through part of the BDA injection site in LPMCv in case SDM22. The white arrow in the subcortical white matter identifies a coalesced bundle of BDA fibers emerging from the injection site and passing dorsal to the claustrum. F) Horizontal section through the contralateral hypoglossal nucleus showing BDA labeled fibers and terminal boutons in the HN in case SDM22. The asterisk in the main panel denotes the location of the higher powered inset in the bottom left hand corner of the panel. The image of the main axon shown in the inset has been rotated 90°. The pull-out sphere shows a higher power (100x) images from the selected region of the nucleus G) Photomicrograph of a coronal section through the BDA injection site in area ProM in case SDM40. The black arrow in the subcortical white matter identifies a bundle of BDA fibers arching over the circular sulcus (CiS). H) Horizontal section through the contralateral hypoglossal nucleus showing BDA labeled fibers and terminal boutons (black arrowheads) in the HN. The asterisk in the main panel denotes the location of the higher powered inset in the bottom right hand corner of the panel. The pull-out sphere shows a higher power (100x) image of labeled boutons in the dorsolateral region of the hypoglossal nucleus (approximating the region identified by the double arrowhead) from a section inferior to the main image. Abbreviations: CiS, circular sulcus; HN, hypoglossal nucleus; ilas, inferior limb of the arcuate sulcus.