Figure 1.
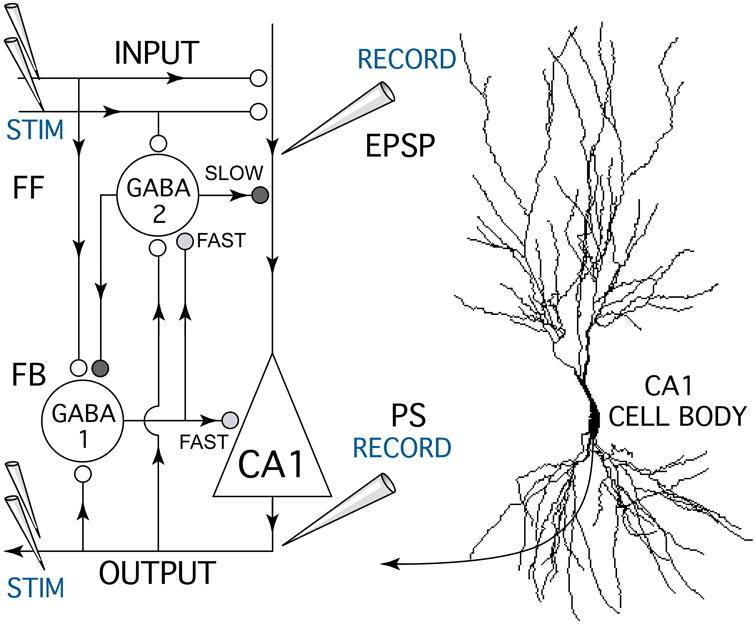
Schematic diagram of the hippocampal CA1 circuit showing the experimental setup used to test anesthetic effects on excitatory glutamate synapses and GABA-mediated inhibitory feedforward (FF) and feedback (FB) synapses. A bipolar stimulating electrode (STIM) was placed on Schaffer-collateral fiber excitatory inputs (INPUT) which make glutamate synapses (white circles) onto CA1 pyramidal neuron apical dendrites. Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) resulting from input stimulation were recorded using a field potential electrode (RECORD) placed in the apical dendrite zone where synaptic currents were generated. A second recording electrode was placed near CA1 neuron cell bodies to measure population spike discharges (PS, OUTPUT) generated in response to Schaffer-collateral synaptic activation. Paired pulse stimuli were used measure anesthetic effects on different forms of GABA-mediated synaptic inhibition (grey and black symbols) generated by inhibitory neurons (GABA 1-FAST & 2-SLOW). Antidromic population spike responses were generated by stimulating CA1 neuron axons (STIM OUTPUT) with a bipolar electrode placed in the alveus. Arrowheads indicate the direction of information flow in the CA1 circuit.
