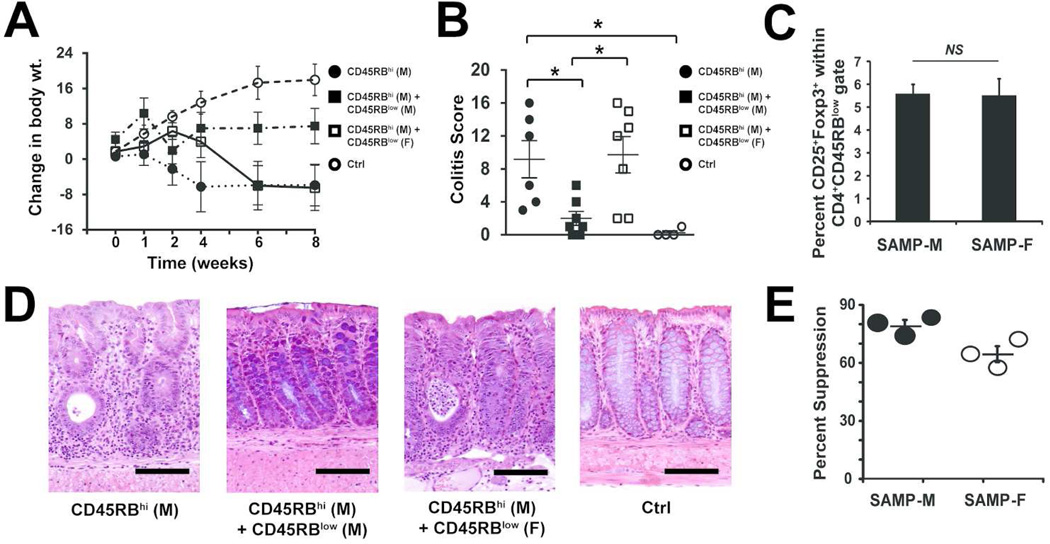
Figure 3. Treg cells from SAMP-F are dysfunctional in vivo and in vitro.
6-wk-old SCID mice were reconstituted with FACS-sorted MLN CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells from SAMP-M alone (● RBhi) or co-transferred with MLN CD45RBlow CD4+ T cells from either SAMP-M (■ RBlow-M) or SAMP-F (□ RBlow-F); vehicle, mock-transferred SCIDs served as controls (○ Ctrl). (A) Changes in body weight are shown in weeks post-transfer and (B) histologic evaluation of colitis is shown at 8 wks post-transfer. Percent change in body weight and composite inflammatory scores are represented as mean ± SEM (*p≤0.05, n=16/group). (C) Mean percentage of CD25+/Foxp3+ cells within the RBlow T cell population of SAMP-M and –F is expressed ± SEM. (D) Representative photomicrographs of colon from indicated mice (scale bar=100 µm; original magnification 20× + 1.25NA). (E) In vitro Treg suppression activity. CD4+CD25− Tconv and CD4+CD25+ Treg cells were isolated from SAMP-M or SAMP-F mice. Tconv were cultured alone or with a 1:1 ratio of Treg for 3 days in the presence of αCD3/αCD28. Percent suppression is expressed as the percentage of Tconv proliferation that was suppressed by co-culture with Treg cells. Each dot represents one experiment (3 pooled mice per experiment) ± SEM.