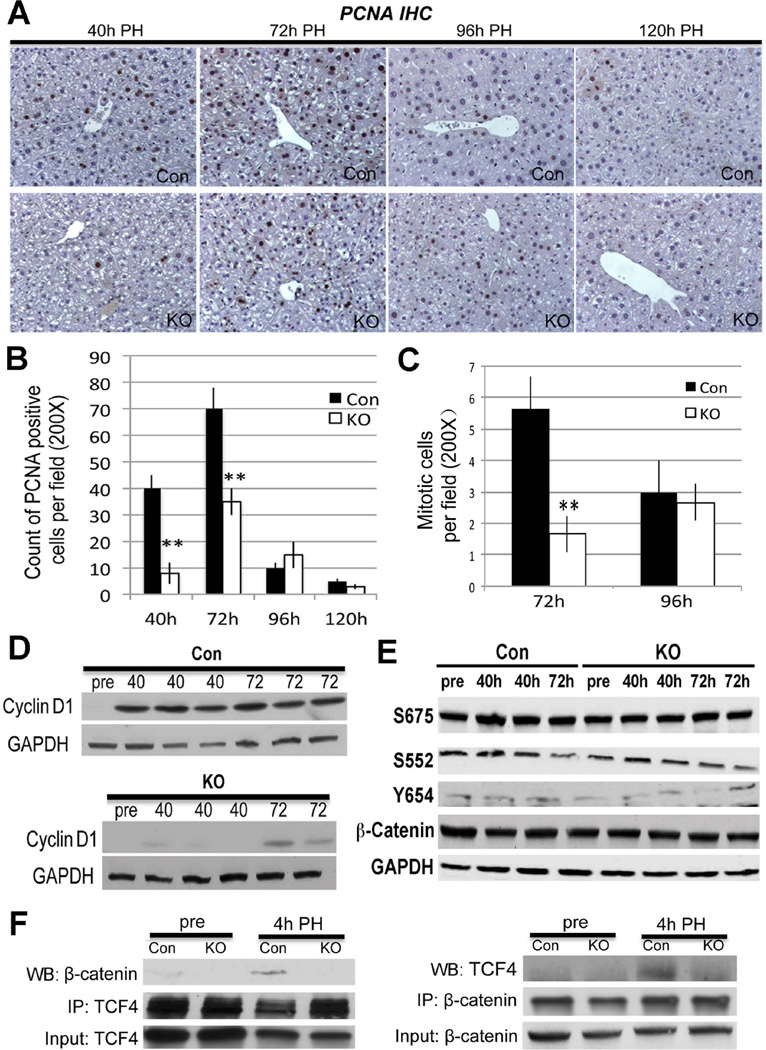
Figure 3. Abolishing Wnt/β-catenin signaling through Lrp5/6 ablation in liver impairs LR after PH.
A. IHC for PCNA identifies several hepatocytes in S-phase at 40 and 72 hours after PH, while only a few trailing hepatocytes were PCNA-positive at 96 and 120 hours. In contrast, Lrp-LKO showed dramatically fewer PCNA-positive hepatocytes at 40 hours with an increase at 72 hours. Like Con, only a few PCNA-positive hepatocytes were detected at later times in Lrp-LKO. (200×)
B. PCNA quantification shows a gradual increase in positive hepatocytes in Lrp-LKO from 40 to 72 hours although these are lower than Con at both times (**p<0.01).
C. Quantification of mitotic figures shows a significantly lower numbers in Lrp-LKO as compared at Con at 72 hours after PH. (**p<0.01)
D. WB shows low protein expression of Cyclin-D1 after PH in Lrp-LKO compared to Con at both 40 and 72 hours although its levels increase in Lrp-LKO at 72 hours.
E. Representative WB shows comparable levels of S675-β-catenin, S552-β-catenin, Y654-β-catenin and total β-catenin in Con and Lrp-LKO livers after PH.
F. Representative WB shows β-catenin and TCF4 association at 4 hours after PH in Con and not Lrp-LKO livers by immunoprecipitation studies. Immunoprecipitation studies were performed by pull down of either β-catenin or TCF4. Respective input controls are included in analysis as well.