Fig. 5.
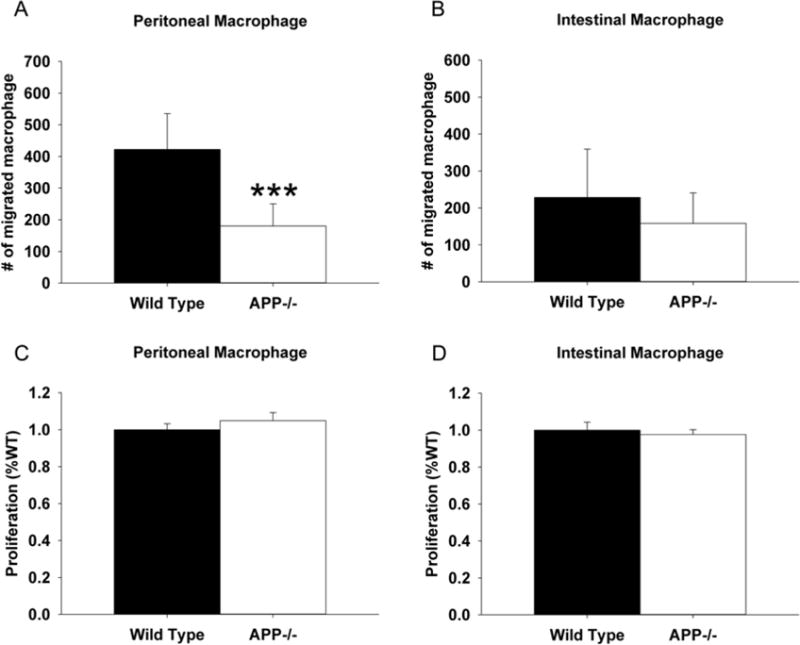
Peritoneal macrophage from APP−/− mice demonstrated significantly decreased migratory ability compared to wild type controls. Non-elicited peritoneal macrophage and intestinal macrophage were isolated from APP−/− and C57BL6/J control mice. (A) For migration assays, macrophage were grown in serum-free DMEM/F12. Cells were added to the top of transwell permeable support inserts placed into collagen coated dishes containing 25ng/mL LPS for 24hr in order to measure migration into the bottom well as assessed by the number of migrated cells. (B) For proliferation assays, macrophage were grown in DMEM/F12 with 10% FBS and 5% horse serum for 72 hours. MTT reduction assays were used as an indirect measure of cellular number to quantify proliferation. Results are mean (+/−SD) from six animals per condition ***p<0.05.
