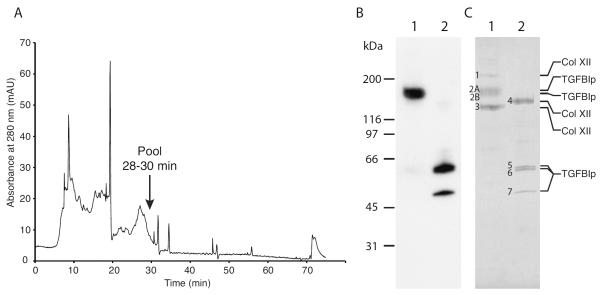
Figure 2. Purification of the high-molecular-weight TGFBIp-containing complex from porcine cornea.
(A) Anion exchange chromatogram from the final step of purification of the high-molecular-weight TGFBIp-containing complex. Collagenase I-digested cornea was initially applied to a heparin affinity column from which all bound protein was dialyzed and applied to an anion exchange column. Fractions 28–30 were pooled and further analyzed. (B) Immunoblot of non-reducing (lane 1) and reducing (lane 2) SDS-PAGE of the pooled fractions containing the 170-kDa TGFBIp-containing complex. (C) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE gel of non-reduced (lane 1) and reduced (lane 2) samples of the purified 170-kDa TGFBIp-containing complex. Protein bands that were analyzed by MALDI-MS and N-terminal sequencing are indicated with numbers 1 to 8 and the identity based on MS-analysis is shown on the right. The characterization of the TGFBIp-containing complex shows that non-covalently bound type XII collagen molecules migrating at 210 kDa and 138 kDa co-purifies with the covalent and reducible 170-kDa TGFBIp:collagen XII complex.