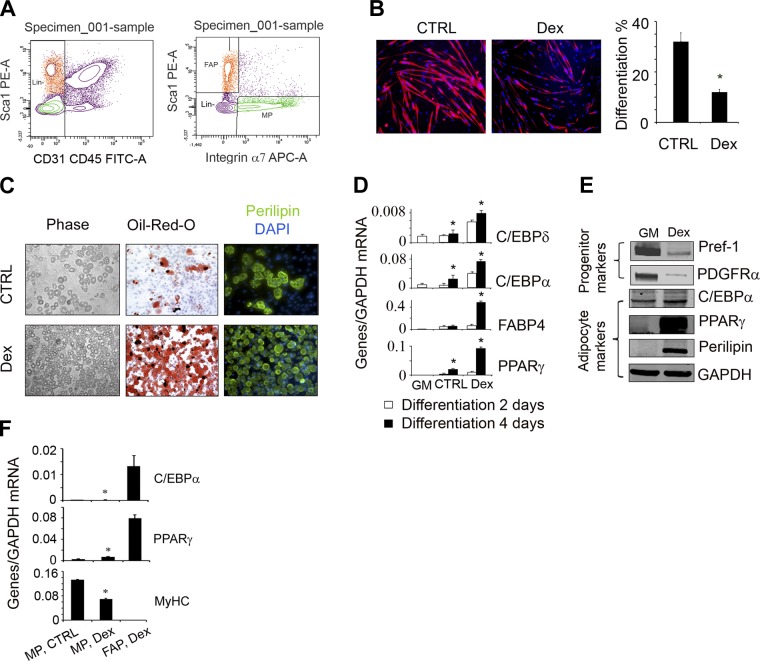
Figure 2.
In vitro, GC only induce differentiation of muscle-derived FAPs into adipocytes. A) Satellite cells (integrin-α7+/CD31−/CD45−/Scal-1−) and FAPs (integrin-α7−/CD31−/CD45−/Scal-1+) were isolated using FACS (left panel; see Materials and Methods). B) Isolated satellite cells were cultured in DM or DM plus Dex and coimmunostained with anti-eMyHC (red). The differentiation index was calculated as the percentage of nuclei within myotubes that stained positively for eMyHC plus the number of eMyHC+ mononuclear cells to the total number of nuclei in the area (right panel; n=3 repeat, medium without Dex). *P < 0.05 vs. control (Ctrl). C) Isolated FAPs were cultured in GM or DM plus Dex; cells were photographed under light microscopy (left panels). At 7 d after treatment, cells were stained with Oil-Red-O (middle panels), or were immunostained with antiperilipin at 14 d after treatment (right panels). D) mRNAs were evaluated by RT-PCR in FAPs (adipogenic differentiation in 2–4 d; n=3 repeat). *P < 0.05 vs. FAPs cultured in GM. E) FAPs were cultured in medium plus Dex for 4 d; protein levels of adipogenic proteins were evaluated by Western blots from the cell lysates. F) Satellite cells and FAPs were cultured in same conditions, and mRNAs from these cells were analyzed by RT-PCR (n=3 repeat).*P < 0.05 vs. FAPs in Dex.