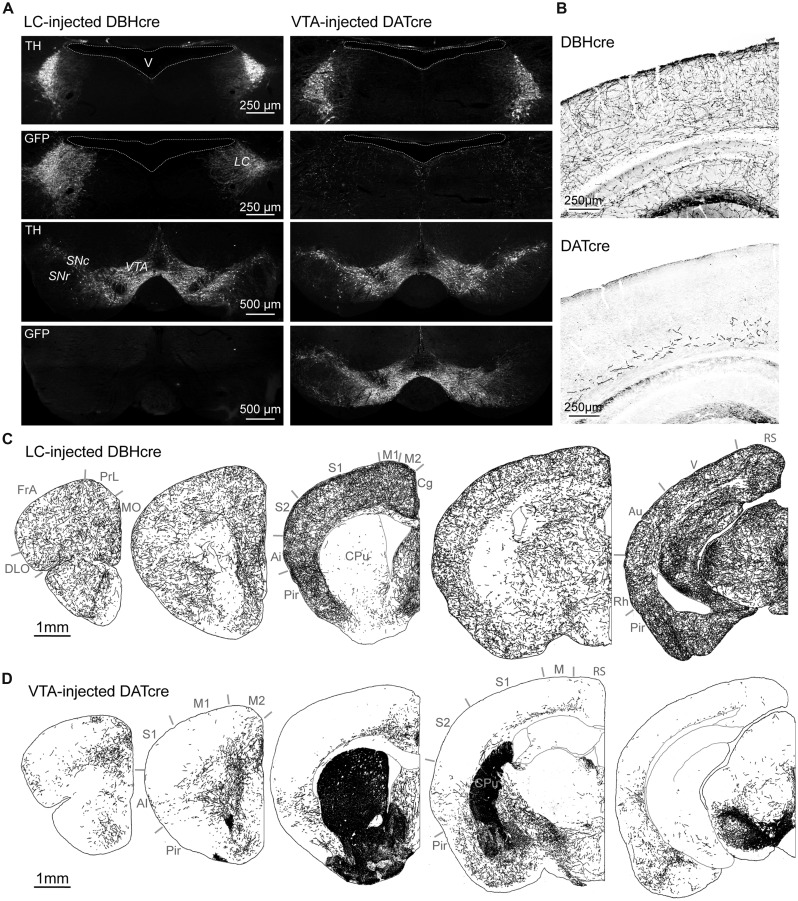
FIGURE 1.
Catecholaminergic projections to the cortex. (A) Immuno labeling against TH and GFP in the LC and VTA 8 weeks after bilateral injection of a Cre-dependent AAV expressing GFP in the LC of DBH-Cre mice or the VTA of DAT-Cre mice. Note that GFP labeling in VTA-injected DAT-Cre mice extends to neighbor DA neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) but is absent from NA neurons of the LC. (B) Immunolabeling of GFP-expressing fibers in the somato-sensory parietal cortex of DBH-Cre and DAT-Cre mice. (C,D) Drawings of NA or DA fibers obtained from immunolabeling of GFP positive fibers in coronal brain sections of LC-injected DBH-Cre and VTA-injected DAT-Cre mice (antero-posterior from left to right). Note the different distribution of NA and DA fibers in cortical areas and caudate-putamen (CPu). Ai: agranular insular cortex; Au: auditory cortex; Cg: cingulate cortex; DLO: dorso-lateral orbital cortex; FrA: frontal association cortex; M1-M2-M: primary or secondary motor cortex; MO: medial orbital cortex; Pir: piriform cortex; PrL: prelimbic cortex; Rh: rhinal cortex; RS: retrosplenial cortex; S1: primary somatosensory cortex; V: visual cortex.