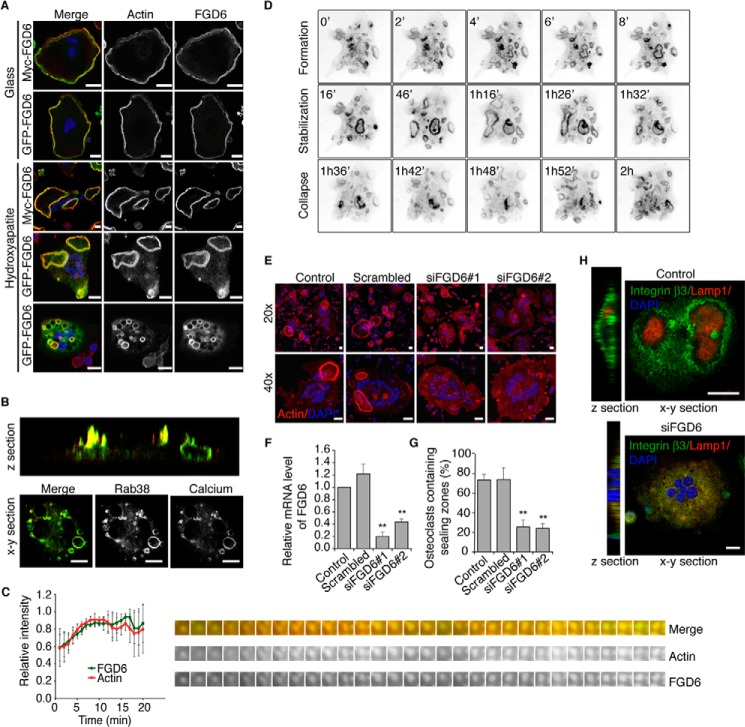
FIGURE 1.
FGD6 localizes to sealing zones and transcytotic vesicles of osteoclasts and regulates their polarity. A, intracellular distribution of Myc- or GFP-tagged FGD6 (green) expressed in osteoclasts grown on glass or ODs. Cells were stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Bars, 20 μm. B, intracellular distribution of GFP-Rab38 (green) and digested calcium (red) in osteoclasts grown on ODs. See also supplemental Videos S1 and S2. C, dynamics of GFP-FGD6 and RFP-Ezrin actin-binding domain at podosomes of osteoclasts grown on glass analyzed by time lapse video microscopy (one frame per min). Fluorescence intensities associated with GFP or RFP on single podosomes were quantified. See also supplemental Video S3. D, dynamics of GFP-FGD6 in osteoclasts grown on ODs analyzed by time lapse microscopy (one frame per min). See also supplemental Video S4. E, osteoclasts grown on ODs were either mock-transfected, or transfected with scrambled siRNAs or with siRNAs targeting FGD6. Cells were stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Bars, 20 μm. F, FGD6 expression levels were quantified by RT-PCR. G, the number of osteoclasts with sealing zones was quantified. Values are mean ± S.D. from 3 experiments (n = 300 osteoclasts per experiment). All groups were compared with control by applying a Dunnett one-way ANOVA test. *, p < 0.05. **, p < 0.01. H, distribution of integrin β3 and Lamp1 in control and FGD6-depleted osteoclasts grown on ODs. Bars, 20 μm. Representative images are shown.