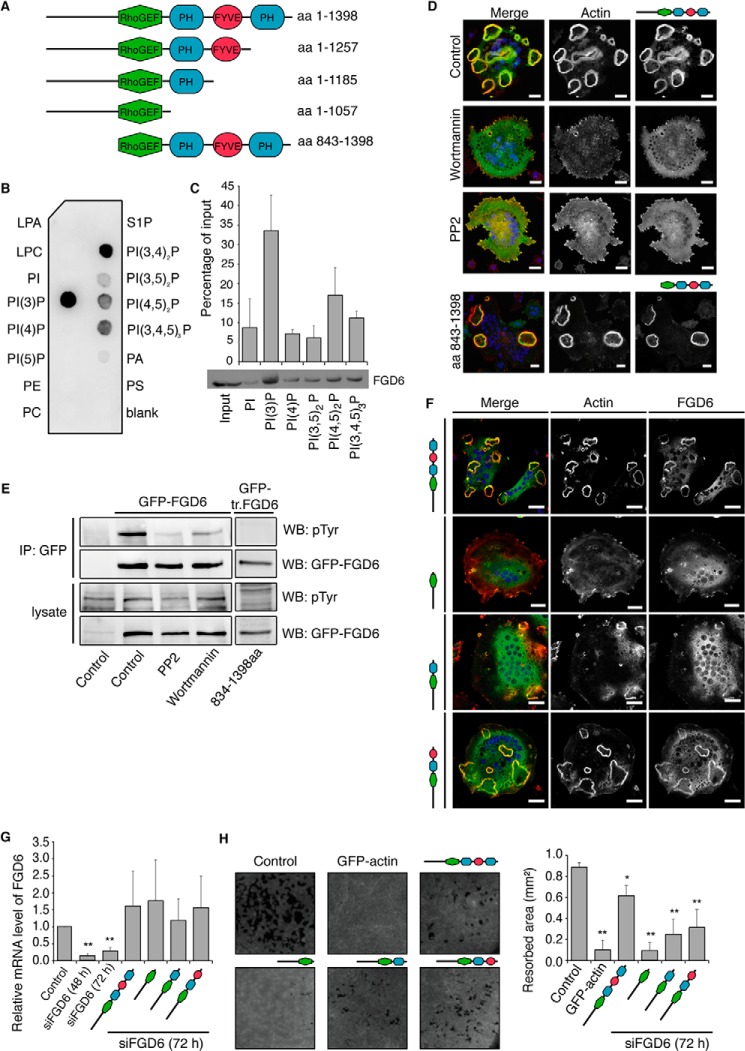
FIGURE 2.
The PH and FYVE domains of FGD6 are required for sealing zone formation and surface resorption. A, the FGD6 mutants used in this study. B and C, binding of His-Myc-tagged FGD6 lacking its N-terminal domain (aa 843–1398) to the indicated lipids present on nitrocellulose strips (B) or liposomes (C). D, osteoclasts grown on ODs expressing GFP-FGD6 full-length or truncated from its N-terminal domain (green) were left untreated or treated with either 500 nm wortmannin or 10 μm PP2 for 1 h. Cells were stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue) and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Bars, 20 μm. E, cell lysates from similarly treated osteoclasts were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP. After Western blotting immunoprecipitates (IP) and cell lysates were probed for GFP-FGD6 or phosphotyrosine. F-H, in osteoclasts depleted from endogenous FGD6 different GFP-tagged FGD6 proteins (wild type and mutants) were expressed as indicated (green). F, cells were stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue), and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Bars, 20 μm. G, expression levels of the FGD6 full-length and mutants were quantified by RT-PCR. Values are mean ± S.D. from 3 experiments. H, the corresponding digested areas on ODs (appearing as black spots on a gray background) were quantified. Values are mean ± S.D. from 3 experiments. All groups were compared with control by applying a Dunnett one-way ANOVA test. *, p < 0.05. **, p < 0.01. Representative images are shown. The abbreviations are: PI, phosphatidylinositol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; S1P, sphingosin-1-phosphate; WB, Western blot.