FIGURE 6.
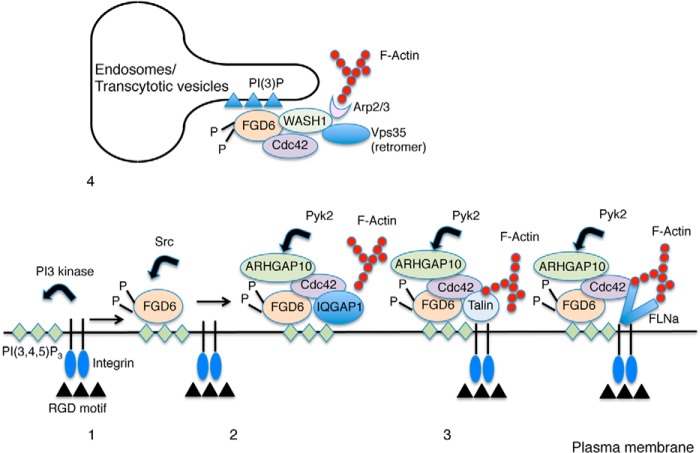
Model of FGD6 function in podosome dynamics and retromer-dependent recycling (1). At the plasma membrane, integrins bind to RGD motifs of extracellular bone matrix proteins. This triggers the activation of the PI 3-kinase, which produces PI(3,4,5)P3 in the vicinity of the engaged integrins (2). Upon Src-dependent phosphorylation, FGD6 binds to PI(3,4,5)P3 and potentially PI(4,5)P2, and exchanges GDP for GTP on Cdc42 (3). FGD6 interacts with IQGAP1, which binds Cdc42 and PI(3,4,5)P3. IQGAP1 can then trigger F-actin polymerization. FGD6 also interacts with Talin-1/2 or Filamin A (FLNa) and can coordinate Cdc42-dependent cell adhesion and F-actin polymerization required for podosome formation. These complexes may contain ARHGAP10 whose GAP activity is inhibited by Pyk2-dependent phosphorylation (4). On early endosomes and transcytotic vesicles, phosphorylated FGD6 binds to PI(3)P and to the WASH complex. FGD6 also exchanges GDP for GTP on Cdc42, which activates WASH. WASH triggers F-actin polymerization to sustain retromer (Vps35)-dependent recycling of membrane components.