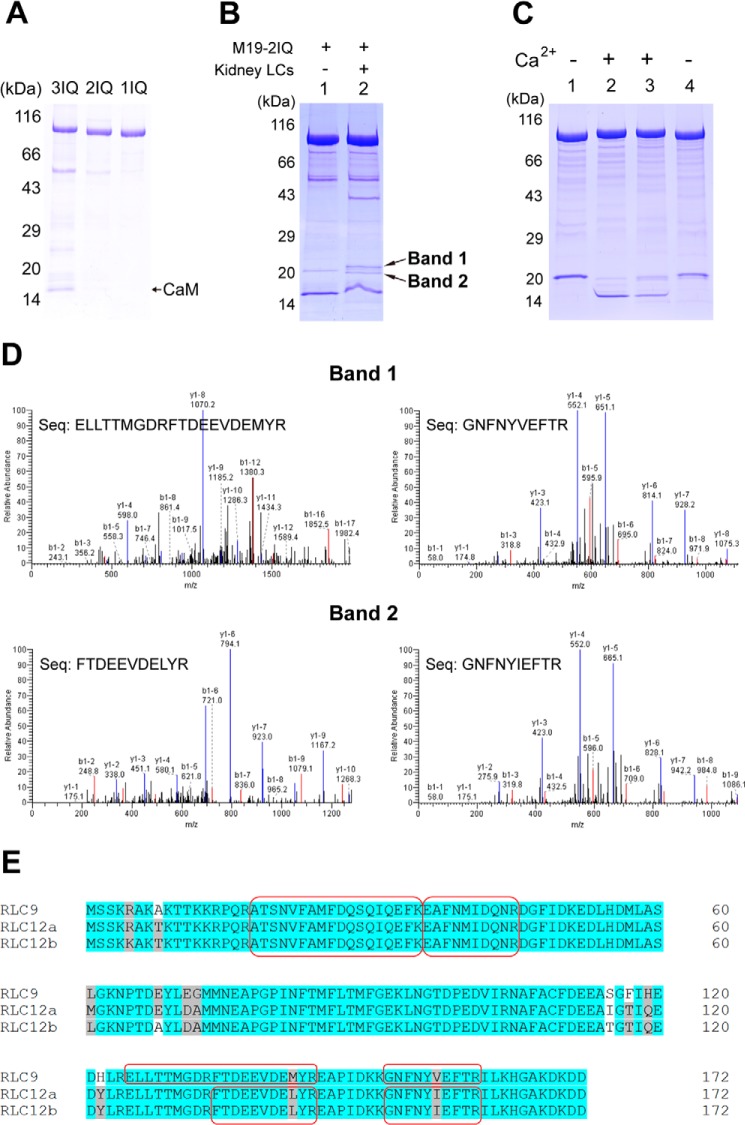
FIGURE 3.
Identification of the light chain of Myo19. A, SDS-PAGE (4–20%) of the purified Myo19-truncated constructs coexpressed with CaM in Sf9 cells. B, SDS-PAGE (4–20%) of M19-2IQ co-purified with crude extract of myosin light chain from mouse kidney. Lane 1, purified M19-2IQ expressed in Sf9 cells; 2, re-purified M19-2IQ after incubated with crude extract of myosin light chain from mouse kidney. Band-1 and band-2 indicate the two specific ∼20-kDa bands co-purified with M19-2IQ. C, CaM gel shift assay of the light chain co-purified with M19-2IQ. Lanes 1 and 2, purified M19-2IQ expressed in Sf9 cells; lanes 3 and 4, re-purified M19-2IQ after incubation with crude extract of myosin light chain from mouse kidney. Lanes 1 and 4 were run under EGTA conditions, lanes 2 and 3 were run under Ca2+ conditions. For details, see ”Experimental Procedures.“ D, MS/MS analysis of band-1 and band-2 in lane 2, the two specific ∼20-kDa bands co-purified with M19-2IQ. Two peptides corresponding to RLC9 and RLC12b were detected in band-1 and band-2, respectively. The sequences of the peptides were shown. E, amino acid sequence alignment of three isoforms of mouse RLC. The sequences shaded in gray are conserved but not identical residues, and the ones in white are non-conserved residues. The peptide sequences identified in MS/MS are boxed.