FIGURE 9.
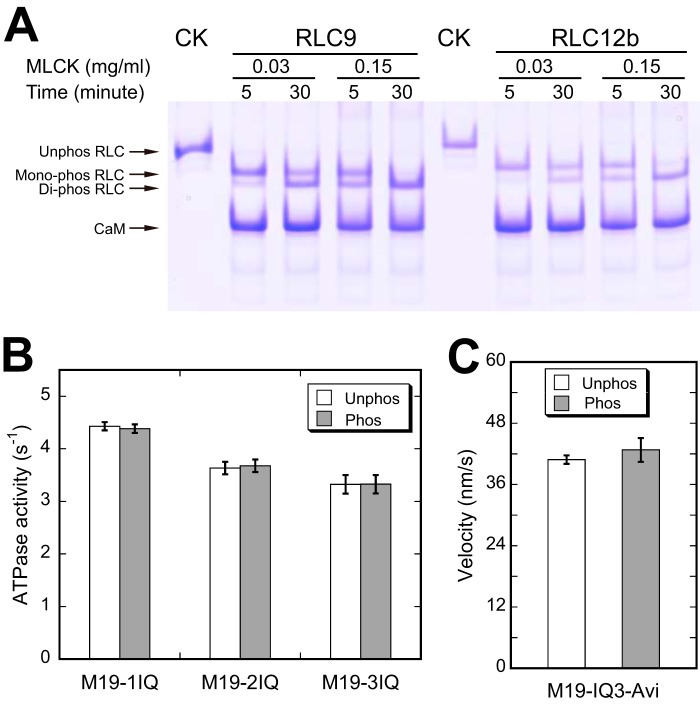
Effects of RLC phosphorylation on the motor function of Myo19. A, phosphorylation of the RLC of M19-3IQ by MLCK. M19-3IQ was co-expressed with RLC9 or RLC12b in Sf9 cells and purified by anti-FLAG affinity chromatography. The purified M19-3IQ/RLC9 or M19-3IQ/RLC12b was incubated with MLCK (0.03 mg/ml) in phosphorylation solution (30 mm Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 50 mm KCl, 1 mm DTT, 1 mm MgCl2, 10 μm CaM, 0.1 mm CaCl2, and 1 mm ATP) at 25 °C for the indicated times. Phosphorylation of RLC was determined by urea/glycerol PAGE and visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. CK represents the unphosphorylated control, which was not treated with MLCK. B, effects of RLC phosphorylation on the actin-activated ATPase activity of Myo19. ATPase assay was performed in 50 mm KCl, 25 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 1 mm MgCl2, 0.25 mg/ml of BSA, 1 mm DTT, 0.5 mm ATP, 2.5 mm phosphoenol pyruvate, 20 units/ml of pyruvate kinase, 40 μm actin, 0.1 mm CaCl2, 2 μm CaM with 0.03 mg/mg of MLCK (phosphorylated conditions) or without MLCK (unphosphorylated conditions) at 25 °C. The reaction was stopped at various times between 4 and 60 min as described under “Experimental Procedures.” C, effects of RLC phosphorylation on in vitro actin-gliding activity of Myo19-3IQ-Avi. Prior to actin-gliding assay, biotinylated M19-3IQ-Avi was phosphorylated by 0.15 mg/ml of MLCK in phosphorylation solution at 25 °C for 5 min. Actin-gliding assay was performed as described in the legend of Fig. 7.