Fig. 6.
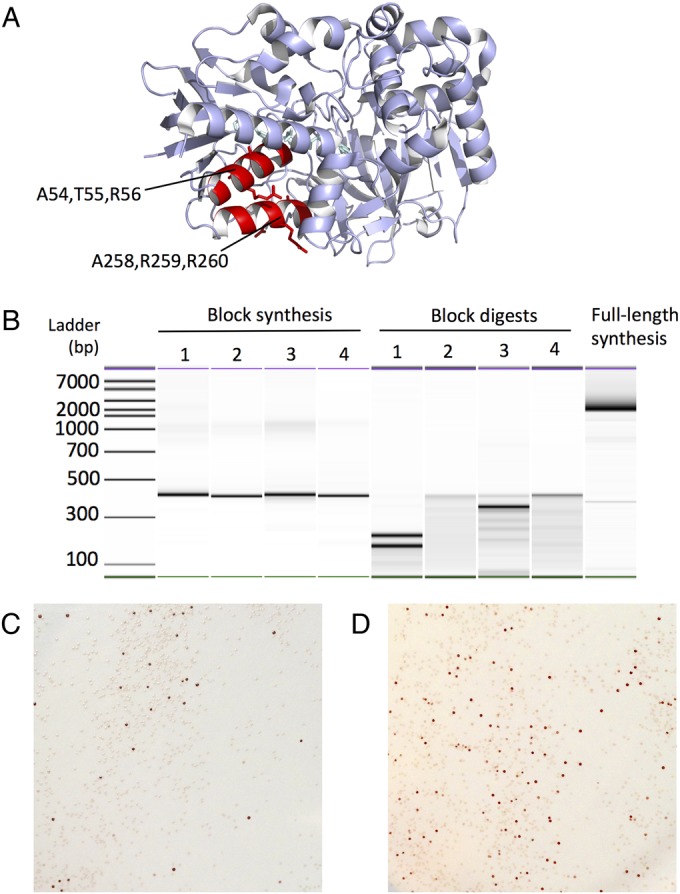
Synthesis of MAO-N variants for functional screening. (A) Two adjacent α-helices were selected for the generation of protein libraries (highlighted in red on the MAO-N D5 structure, PDB code: 2VVM). The ATR (Residues 54–56) and ARR (258–260) side chains are shown. (B) The MAO-N sequence encoding six variant codons was synthesised using the SpeedyGenes method. The observed difference in digestion of Fragments 1 and 3 is due to the cleavage of the variant sequences encoded within these fragments. Oligonucleotides 5 (encoding variant codons for residues ATR) and 22 (for ARR) were ‘spiked’ into the final OE-PCR at 6 nM prior to the full-length synthesis. (C) The synthesised sequence was expressed in E. coli and screened for MAO-N activity. (D) Another MAO-N variant encoding variant codons for the ATR sequence only was also synthesised and screened for MAO-N activity. Both variants show a variation in activity which were then analysed using DNA sequencing, illustrating that SpeedyGenes can synthesise variant libraries de novo for direct recombinant expression and functional screening.
