Figure 6.
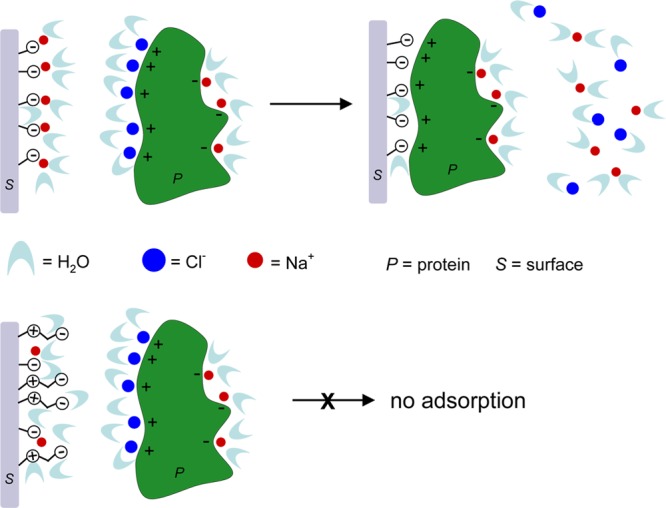
Cartoon for the ion-coupled adsorption mechanism of a protein with a positive charge onto a negatively charged hydrophilic substrate, such as a silicon wafer (where the charge comes from ionized silanols). Upper: The adsorption of protein is facilitated by the release of counterions and the formation of ion pairs between the sorbent and the adsorbate. Lower: A neutral surface (zwitterion or PEG) has no surface ions associated with it. The binding of protein to the surface will not result in a net increase in entropy due to counterion release, and thus adsorption is not preferred. Note that some net charge is still associated with the original surface but is inaccessible due to a steric barrier.
