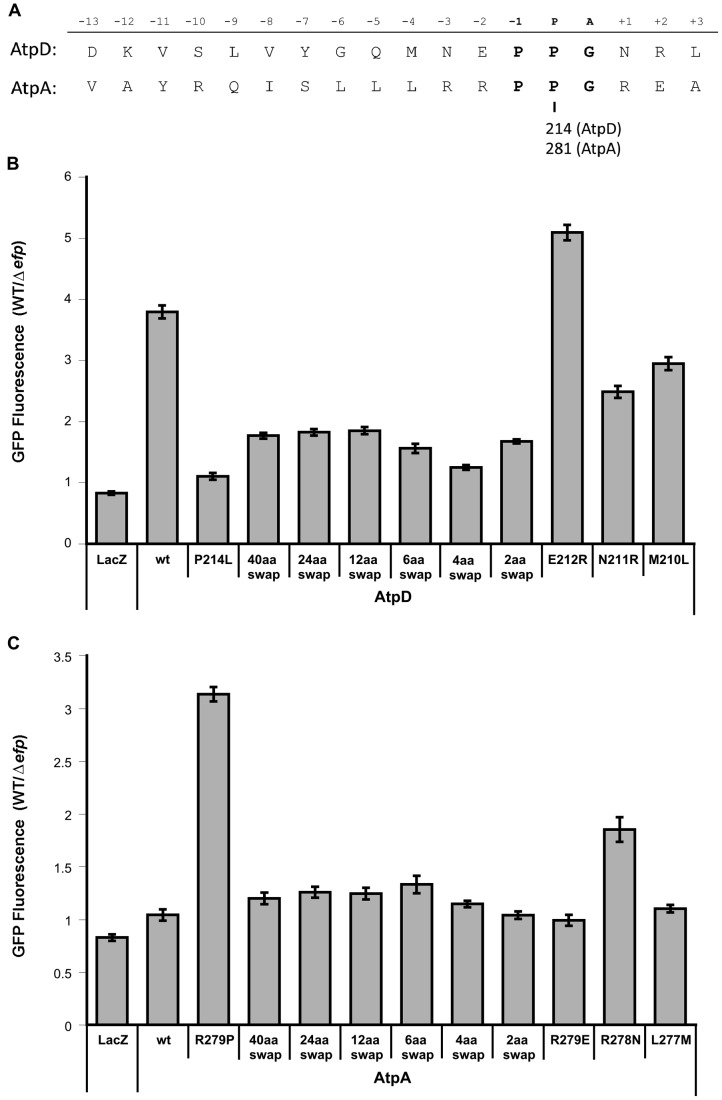
Figure 5. Effect of upstream residues on the EF-P dependence of AtpD and AtpA synthesis.
A) Sequences (Salmonella Typhimurium) of AtpD and AtpA in proximity to their PPG motifs (bold). The relative position when the glycine of PPG occupies the A site is shown above. The amino acid position of the second proline of the PPG motif in each protein is indicated below. B) Fluorescence ratios comparing expression of plasmid-borne AtpD-GFP translational fusions in wild-type (WT) and efp mutant Salmonella. ‘Swap’ constructs indicate swap-in of AtpA sequence for the specified number of amino acids upstream of the PPG motif. LacZ, unmodified (wt), P214L and R279P constructs from Figure 4 are included for comparison. Ratios show WT/Δefp for GFP fluorescence at 10 hours post-inoculation normalized to optical density (600 nm). The mean of at least three biological replicates is shown and error bars indicate one standard deviation. C) As in B, but with AtpA-GFP translational fusion constructs with swap-in of AtpD upstream sequence.