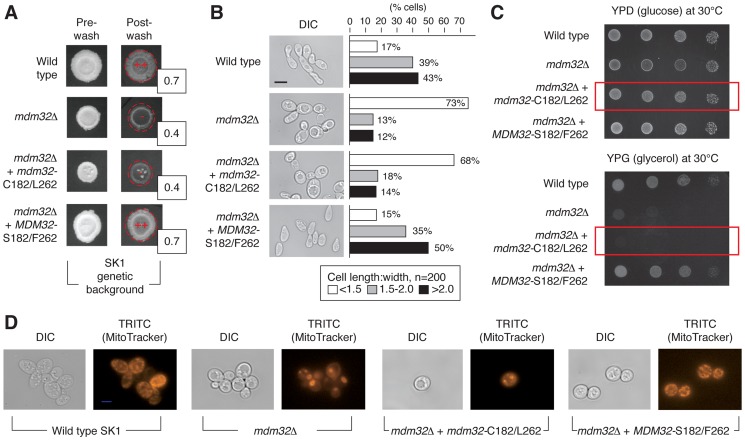
Figure 5. Phenotypic consequences of variation in Mdm32p residues 182 and 262.
A) Invasive growth assays of wild-type and mdm32 mutants in the SK1 background were performed as described previously. Invasive growth levels were quantified by determining the ratio of the pixel intensity of images of the spotted cultures before and after plate washing, and these ratios are indicated in the boxes to the lower right of the spotted cultures post-washing. B) Introduction of the BY4741-encoded MDM32-C182/L262 allele into SK1 results in decreased cell elongation relative to wild type. In this analysis, cells were scraped from colonies into a suspension for imaging of cell morphology as described previously. C) A strain of SK1 carrying the S288C-encoded allele of MDM32 exhibits a growth defect on medium containing the non-fermentable carbon source glycerol. Cells from the indicated strains were grown overnight in glucose- containing medium, and subsequently, 10-fold serial dilutions were spotted onto plates containing glucose (YPD) or glycerol (YPG) as a carbon source. YPD plates were incubated for 2 days and YPG plates for 3 days at the indicated temperatures. D) Analysis of mitochondrial network structure in a mutant strain of the SK1 background carrying the BY4741-encoded MDM32-C182/L262 allele. As visualized by staining with a mitochondrial dye, the mitochondrial network is compact and collapsed in a strain deleted for MDM32 and in the SK1 mutant carrying the BY4741 allele.