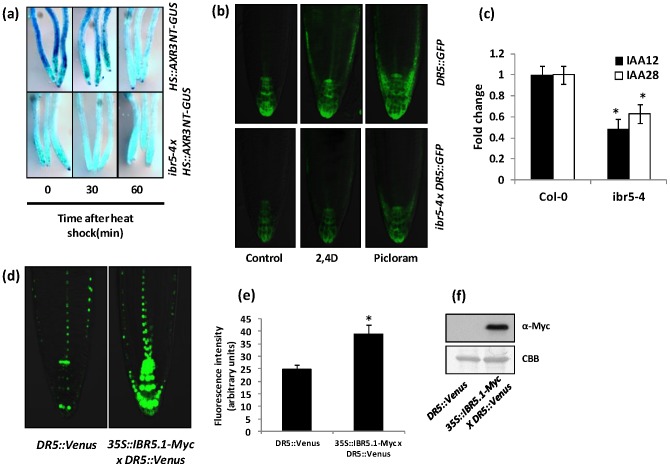
Figure 3. Aux/IAA degradation and auxin induced DR5::GFP expression.
a) Rapid degradation of AXR3NT-GUS in ibr5-4. Four day old light grown wild type Col-0 and ibr5-4 seedlings carrying HS::AXR3NT-GUS were heat shocked for two hours, fixed after the indicated time intervals and stained for GUS. b) Reduced DR5::GFP expression in ibr5-4. Four day old light grown wild type Col-0 or ibr5-4 seedlings carrying the DR5::GFP auxin inducible reporter were used. Seedlings were treated with mock (ethanol/DMSO), 100 nM 2,4D or 10 µM picloram for 3 hrs and imaged using Olympus FV1000 confocal microscopy. c) Expression of IAA12 and IAA28 were assessed by qRT-PCR using 4 day old Col-0 and ibr5-4 seedlings. UBA (AT1G04850) was used as the internal control. Expression levels were normalized against wild type Col-0. Error bars indicate standard deviations from the mean. Stars indicate that the means differ significantly from the respective control (ANOVA, P<0.05). d) Increased DR5::Venus expression in IBR5.1-Myc background. Four day old light grown wild type Col-0 or IBR5.1-Myc transgenic seedlings carrying DR5::Venus were used. Seedlings were imaged using Olympus FV1000 confocal microscopy. e) Quantitative analysis of Venus expression. Expression of Venus was quantified using ImageJ software. Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean. Stars indicate that the means differ significantly from the control (n = 15, Student's t-test, P<0.05). f) Expression of IBR5.1-Myc in DR5::Venus lines. Total protein was isolated from homozygous seedlings carrying IBR5.1-Myc and DR5::Venus. IBR5.1-Myc was visualized by western blotting using anti-Myc antibody.