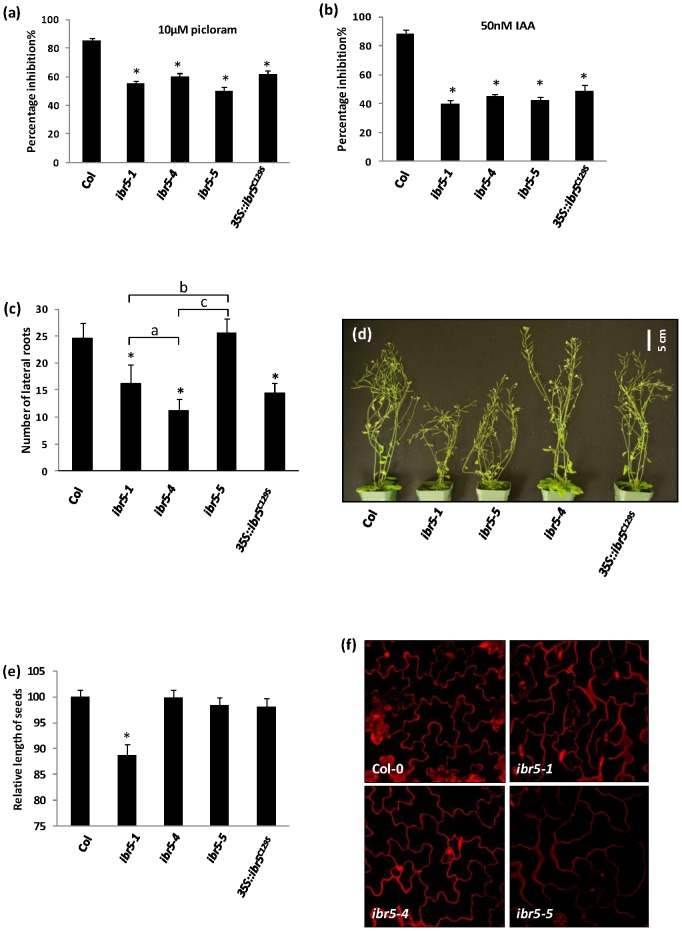
Figure 4. Characterization of new ibr5 alleles.
a–b) Inhibition of primary root elongation by auxin. Seedlings were grown on unsupplemented ATS media for four days and transferred onto ATS containing the indicated concentrations of a) picloram, b) IAA. Seedlings were grown for four additional days, and the length of the primary root was measured. Results were normalized against unsupplemented media. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Stars indicate the means that differ significantly from the control (n = 15). c) Number of lateral roots in ibr5 mutants. Seedlings were grown on unsupplemented ATS media for 12 days, and the number of primordia emerged from the primary root were counted as lateral roots using a dissecting microscope. Error bars indicate standard deviations of the means (n = 20). d) Adult plant morphology of six week old ibr5 alleles grown in continuous light at 25°C. e) Seed size of ibr5 mutants. Dried mature seeds were photographed and the lengths of the seeds were measured using ImageJ software. Error bars indicate standard deviations of the means (n = 20). Stars indicate the means that differ significantly from the control; letters indicate the samples that differ significantly from each other (ANOVA, Tukey's HSD, P<0.05). f) Interdigitation of leaf epidermal pavement cells of ibr5 alleles. Propidium iodide stained lower epidermis of seven-day old cotyledons were imaged.