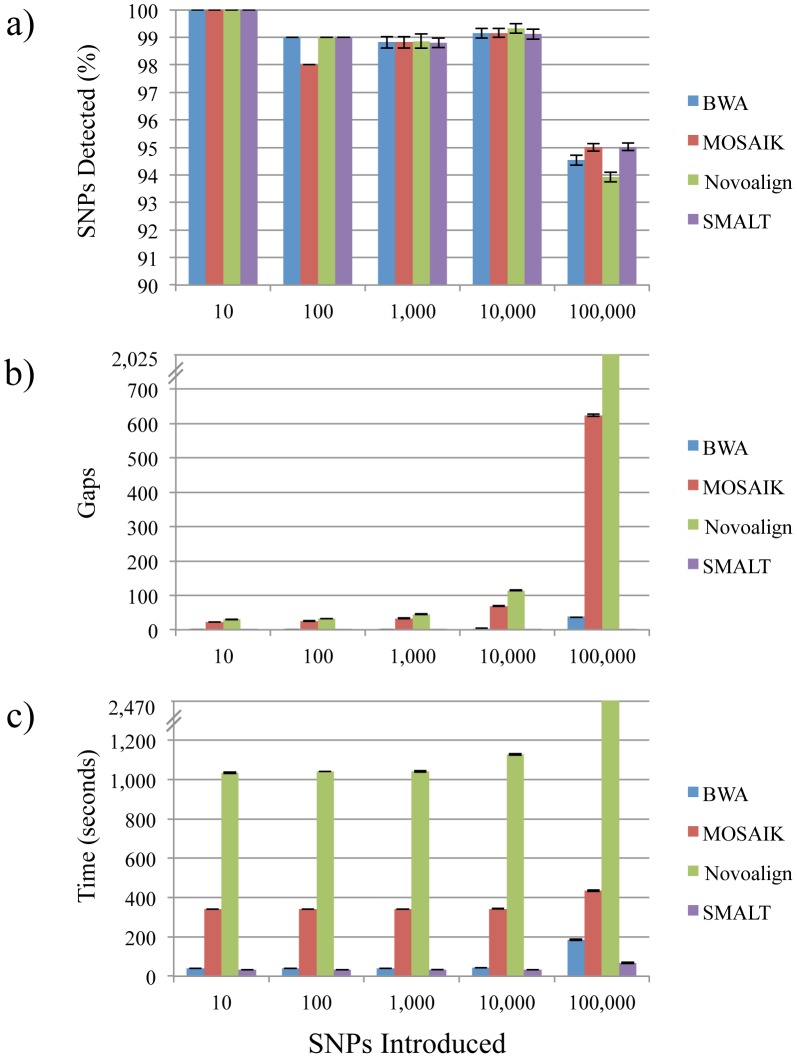
Figure 1. Comparison of consensus sequences calculated from assemblies of simulated Illumina short-read data aligned to references of different genetic distances with four reference-guided assemblers.
Ten sets of simulated sequencing reads were generated using a Listeria monocytogenes strain 08-5578 chromosome sequence obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information archive as a reference. Nucleotide variants were randomly introduced (101–105) in silico to the 08-5578 chromosome sequence to simulate the presence of SNPs in five reference sequences. The performance of four reference-guided short-read sequence assemblers (BWA, MOSAIK, Novoalign, and SMALT) was assessed by averaging the percentages of true SNPs detected (a) and the numbers of gaps present (b) in the consensus sequences generated from alignments of the ten sets of reads. In addition, average assembly processing times are provided (c).