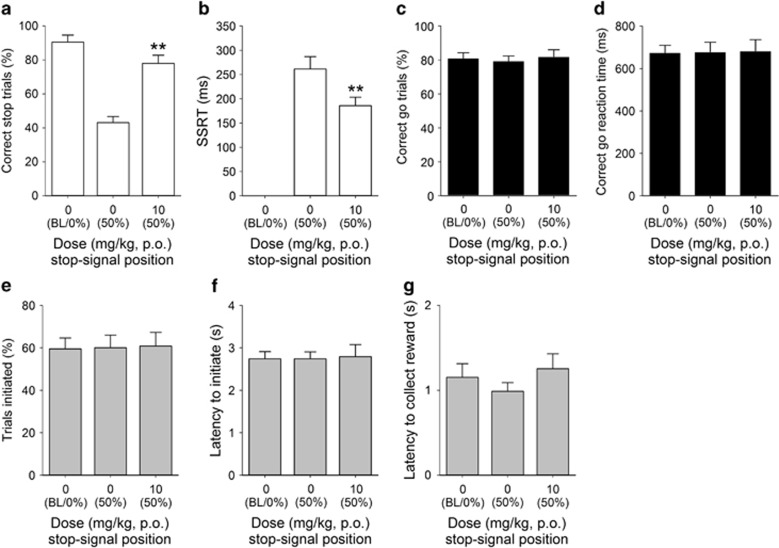
Figure 4.
Effects of COUMATE administration (10 mg/kg) on stop-signal reaction time task performance in adult male MF1 mice (n=11). COUMATE treatment increased the proportion of correctly stopped trials (a) and decreased the SSRT (b). Effects of COUMATE were specific to the stop response, as there were no effects on the proportion of correct go trials performed (c) or correct go reaction time (d); nor were there any group effects on the number (e) or latency (f) to initiate trials, or in the latency to collect reinforcer (g). Baseline data (BL ie, mean of the five sessions immediately preceding each drug treatment session) when the stop-signal presentation were concurrent with the start of the go response (0%) are shown for illustrative purposes and were not included in the statistical analysis. *** and ** denote P<0.01 and P<0.001, respectively, for significant pairwise differences between drug treatments.