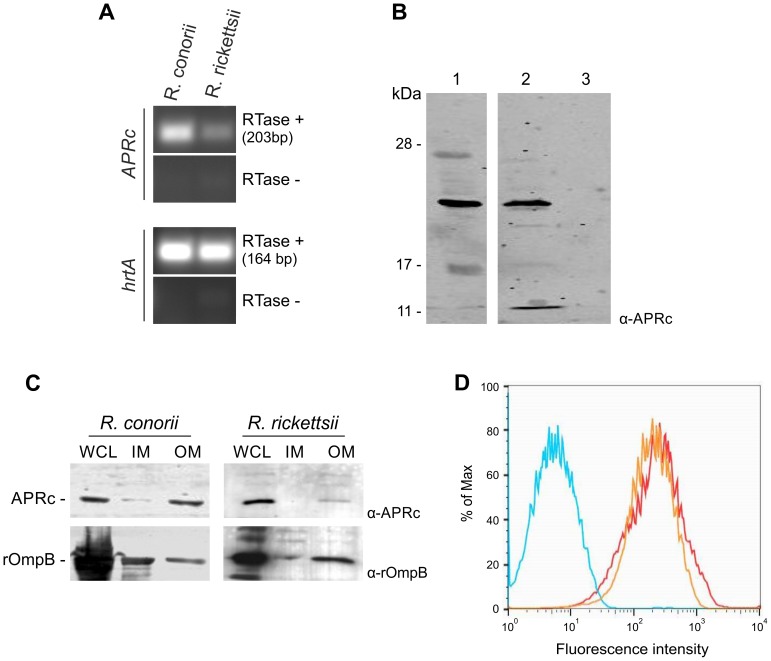
Figure 7. RC1339/APRc is expressed in Rickettsia conorii and Rickettsia rickettsii and accumulates at the outer membrane in both species.
(A) RT-PCR analysis of RC1339/APRc expression on rickettsial spp.. The housekeeping gene hrtA (17 kDa surface antigen) was used as a control. The negative control for the cDNA synthesis lacking reverse transcriptase is identified by (RTase -). Rickettsial species are identified on the top and the gene names are shown on the left side of the agarose gel. (B) A whole cell lysate from R. rickettsii (1) and insoluble (2) and soluble (3) fractions from R. conorii extracts were isolated and then subjected to Western Blot analysis with anti-APRc antibody. A specific band with approximately 21 kDa was detected. (C) Whole cell lysates (WCL), inner (IM) and outer membrane (OM) fractions from sarkosyl treatment of R. rickettsii and R. conorii extracts were isolated and then subjected to Western Blot analysis with anti-APRc and anti-rOmpB antibody. APRc shares the same localization of rOmpB, an internal marker for outer membrane of Rickettsia spp. Molecular mass markers in kilodaltons (kDa) are shown on the left. (D) For flow cytometric analysis of APRc expression in R. conorii, fixed bacteria were queried for deposition of anti-APRc (orange trace), negative control lacking primay antibody (blue trace), or the positive control anti-OmpB (red trace), a known rickettsial surface protein. After incubation with fluorescent secondary antibody, both anti-APRc and anti-OmpB detected on the bacterial surface (increased fluorescence), indicating accessibility of these target proteins to exogenously applied antibody.