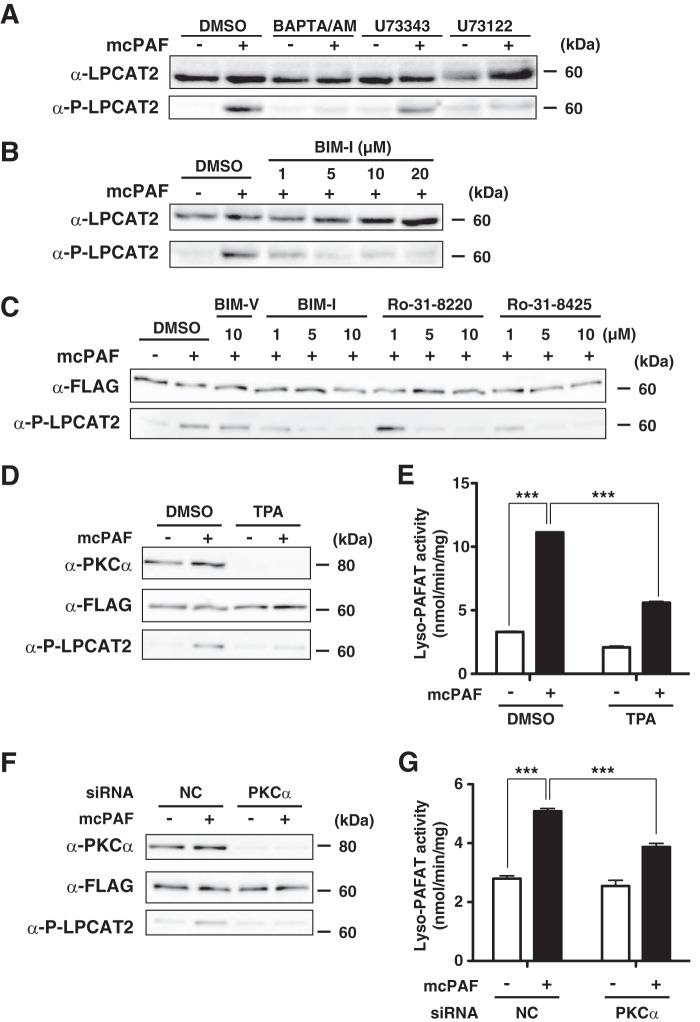
FIGURE 4.
Conventional PKC-dependent LPCAT2 phosphorylation. Peritoneal macrophages were preincubated with or without inhibitors and subsequently stimulated with 200 nm mcPAF for 30 s. Microsomal proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis. A, pretreatment with 10 μm BAPTA/AM or 10 μm U73122, but not an inactive analog, U73343, abolished LPCAT2 phosphorylation. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide. B, pretreatment with the PKC inhibitor BIM-I inhibited mcPAF-induced LPCAT2 phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. 5 μm BIM-I was sufficient to achieve maximum inhibition. C, CHO-S-PAFR cells transfected with FLAG-LPCAT2 were preincubated with or without PKC inhibitors for 1 h and stimulated with 200 nm mcPAF for 30 s. Western blot analysis showed that each of the three different PKC inhibitors abolished the phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. Pretreatment with BIM-V, an inactive analog of BIM-I, had no effect. D, CHO-S-PAFR cells transfected with FLAG-LPCAT2 were pretreated with 100 nm TPA for 24 h and stimulated with mcPAF. TPA decreased PKCα protein and phosphorylation of LPCAT2 by mcPAF. E, pretreatment with TPA also resulted in reduced lyso-PAFAT activation following mcPAF stimulation, as measured by incorporation of acetyl-CoA into deuterium-labeled PAF. F and G, PKCα siRNA and FLAG-LPCAT2 were cotransfected into CHO-S-PAFR cells. Reduction of PKCα protein expression by its siRNA transfection was associated with reduced mcPAF-induced phosphorylation of LPCAT2 and lyso-PAFAT activation following mcPAF stimulation. Results are expressed as the mean + S.D. of an experiment performed in triplicate. NC, negative control. ***, p < 0.001; analysis of variance and Tukey's multiple comparison test. Three (A–C) or four (D--G) independent experiments were performed with similar results.